The Ryton® PPS Family
The highly stable chemical bonds of Poly(p-phenylene sulfide) (PPS) molecular structure impart a remarkable degree of molecular stability toward both thermal degradation and chemical reactivity.
PPS is a semi-crystalline polymer with a high crystalline melting point of about 285°C (545°F). Because of its molecular structure, PPS also tends to char during combustion, making the material inherently flame retardant.
Discover all Ryton® PPS grades
Distinctive Properties
Ryton® PPS (polyphenylene sulfide) compounds offer a unique combination of properties and a cost/performance balance unmatched by other engineering thermoplastics.
Thermal stability
Ryton® PPS has a very high-temperature capability, with a long-term range above 200°C (392°F) and short-term resistance to temperatures up to 260°C (500° F). As shown in the table below, UL thermal indices for Ryton® PPS go up to 240 °C (464 °F).
Dimensional stability
Even complex parts can be molded with very tight tolerances and will maintain dimensional stability even at elevated temperatures and in harsh chemical environments.
Chemical resistance
Ryton® PPS offers excellent resistance to a broad spectrum of chemicals and has no known organic solvent under 200 °C (392 °F). This allows the material to thrive in highly corrosive environments, including all automotive and electronic processing fluids.
Non-Flammability
Ryton® PPS compounds are inherently flame resistant. Most Ryton® PPS compounds have UL 94 V-0 and many have UL 94 5VA non-flammability ratings without using flame retardant additives. The limiting oxygen index of Ryton® PPS compounds is about 50%, making them among the most flame-resistant plastics.
When comparing flammability ratings of engineering plastics, it is important to note that many require flame retardant additives to be classified UL 94 V-0.
Inherent flame retardancy
Most Ryton® PPS compounds have UL94 V-0 flammability ratings without flame retardant additives.
Chemical Properties
The chemical resistance of Ryton® PPS is well known to be outstanding, even at elevated temperatures. However, being an organic polymer, PPS can be affected by some chemicals under certain conditions.
Over the years, we have accumulated a large database on exposure of Ryton® PPS to a wide variety of chemicals. Although it is not possible to test every chemical, we have seen that chemicals having similar structures and/or properties tend to have similar effects on Ryton® PPS compounds.
If you require further information, our technical experts can provide opinions about the compatibility of Ryton® PPS compounds or Ryton® PPS Alloy compounds with particular chemical environments.
An extensive alphabetical list of chemicals with our best general recommendations regarding their compatibility with Ryton® PPS compounds.
Chart Legend
The chart below provides an alphabetical list of chemicals along with our best general recommendations regarding their compatibility with Ryton® PPS compounds. The type face in which the chemical name is printed indicates the extent of available test data:
- [1]: extensive, long-term test data
- [2]: We have no actual test data, our recommendations are based on compatibility similar chemicals
- All others: We have limited, short-term test data
Chemical compatibility is expressed in four general classifications:
- Acceptable: suitable for extensive exposure even at elevated temperatures
- Questionable at Elevated Temperatures: caution against extensive exposure to these chemicals at temperatures above 65°C (150°F)
- Avoid Use of Mineral Filled Grades: acidic chemicals are likely to dissolve common mineral fillers
- Avoid Exposure: not recommended to use in service with these chemicals except under the limitations cited
Chemical Compatibility Chart
| Chemical | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Acetaldehyde [2] | Acceptable |
| Acetic Acid, 10% | Acceptable |
| Acetic Acid, 100% (Glacial) | Acceptable |
| Acetic Anhydride | Acceptable |
| Acetone [2] | Acceptable |
| Acetonitrile | Acceptable |
| Acetophenone | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Acetyl Chloride | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Acetylene [2] | Acceptable |
| Acid Mine Water [2] | Acceptable |
| Acrylic Acid [2] | Acceptable |
| Aluminum Chloride | Acceptable |
| Aluminum Sulfate | Acceptable |
| 2-Aminoethanol | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Ammonia, anhydrous [2] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Ammonium Chloride | Acceptable |
| Ammonium Hydroxide | Acceptable |
| Ammonium Nitrate | Acceptable |
| Ammonium Sulfate | Acceptable |
| Amyl Acetate | Acceptable |
| Amyl Alcohol | Acceptable |
| Antifreeze [1] | Acceptable |
| Aniline [1] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Aqua Regia | Avoid Exposure |
| Asphalt Emulsions [2] | Acceptable |
| Barium Chloride | Acceptable |
| Barium Hydroxide [2] | Acceptable |
| Barium Sulfate [2] | Acceptable |
| Benzaldehyde [1] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Benzene [2] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Benzene Sulfonic Acid | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Benzoic Acid [2] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Benzonitrile [1] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Benzoyl Chloride [2] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Benzyl Chloride | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Black Liquor (from pulpwood) [2] | Acceptable |
| Borax | Acceptable |
| Brake Fluid [1] | Acceptable |
| Bromine [1] | Avoid Extensive Exposure above 0.1% |
| Butadiene [2] | Acceptable |
| Butane [2] | Acceptable |
| 2-Butanone (Methyl Ethyl Ketone) [1] | Acceptable |
| Butyl Acetate | Acceptable |
| n-Butyl Alcohol [1] | Acceptable |
| Butyl Ether [1] | Acceptable |
| Butyl Phthalate | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Butylamine [1] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Butylene [2] | Acceptable |
| Calcium Chloride | Acceptable |
| Calcium Nitrate | Acceptable |
| Calcium Sulfate [2] | Acceptable |
| Carbon Dioxide | Acceptable |
| Carbon Disulfide [2] | Acceptable |
| Carbon Tetrachloride [1] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Carbonated Water [2] | Acceptable |
| Carbonic Acid [2] | Acceptable |
| Cellosolve | Acceptable |
| Chlorine [1] | Avoid Extensive Exposure above 0.1% |
| Chlorobenzene | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| 2-Chloroethanol | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Chloroform [1] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Chlorophenol, 5% Aqueous | Acceptable |
| Chlorosulfonic Acid | Avoid Extensive Exposure |
| Chromic Acid | Avoid Extensive Exposure |
| Clorox (5.25% Sodium Hypochlorite) [1] | Acceptable |
| Copper Chloride | Acceptable |
| Copper Sulfate [2] | Acceptable |
| Cottonseed Oil [2] | Acceptable |
| m-Cresol | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Cresyl Diphenyl Phosphate [1] | |
| Crude Oil (aromatic) [1] | Acceptable |
| Cyclohexane | Acceptable |
| Cyclohexanol [1] | Acceptable |
| Cyclohexanone | Acceptable |
| Detergents [2] | Acceptable |
| 1,2- Dichloroethane [1] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Dichloromethane | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Diesel Fuel [1] | Acceptable |
| Diethanolamine, 25% [1] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Diethyl Ether [2] | Acceptable |
| Diisobutylene | Acceptable |
| Dimethyl Phthalate | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Dimethyl Sulfoxide | Acceptable |
| Dimethylaniline | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| N,N-Dimethylformamide | Acceptable |
| Dioctyl Phthalate | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| p-Dioxane [1] | Acceptable |
| Diphenyl Ether [2] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Dowtherm [1] | Acceptable |
| Engine Oil [1] | Acceptable |
| Epichlorohydrin | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Ethane [2] | Acceptable |
| Ethanolamine | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| 2-Ethoxyethanol | Acceptable |
| Ethyl Acetate [1] | Acceptable |
| Ethyl Alcohol (Ethanol) [1] | Acceptable |
| Ethyl Chloride [2] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Ethyl Ether [2] | Acceptable |
| Ethyl Mercaptan [2] | Acceptable |
| Ethylene [2] | Acceptable |
| Ethylene Chloride | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Ethylene Chlorohydrin | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Ethylene Dichloride | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Ethylene Glycol [1] | Acceptable |
| Ethylene Glycol Monoethylether | Acceptable |
| Ethylenediamine | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Ferric Chloride | Acceptable |
| Ferrous Chloride [2] | Acceptable |
| Fluorosilicic Acid, 25% | Acceptable |
| Formaldehyde | Acceptable |
| Formic Acid | Acceptable |
| Freon [1] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Fuel Oil [2] | Acceptable |
| Furan | Acceptable |
| Furfural | Acceptable |
| Gasohol (Gasoline/Alcohol) | Acceptable |
| Gasoline [1] | Acceptable |
| Glycolic Acid | Acceptable |
| Heptane | Acceptable |
| Hexane [2] | Acceptable |
| Hexene [2] | Acceptable |
| HFC-134a | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Hydraulic Fluid, Aircraft [1] | Acceptable |
| Hydrazine [2] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Hydrobromic Acid [2] | Avoid Extensive Exposure above 0.1% |
| Hydrochloric Acid [1] | Avoid Extensive Exposure above 0.1% |
| Hydrofluoric Acid | Avoid Extensive Exposure above 0.1% |
| Hydrogen Gas [2] | Acceptable |
| Hydrogen Peroxide [2] | Avoid Extensive Exposure above 5% |
| Hydrogen Sulfide | Acceptable |
| Iodine [2] | Avoid Extensive Exposure above 0.1% |
| Isopropyl Alcohol | Acceptable |
| Isopropyl Mercaptan [2] | Acceptable |
| Jet Fuel | Acceptable |
| Kerosene | Acceptable |
| Lactic Acid | Acceptable |
| Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) [2] | Acceptable |
| Lithium Bromide [2] | Acceptable |
| Lubricating Oil [2] | Acceptable |
| Magnesium Chloride | Acceptable |
| Magnesium Hydroxide [2] | Acceptable |
| Methane [2] | Acceptable |
| Methoxy Propanol [1] | Acceptable |
| Methyl Acrylate [2] | Acceptable |
| Methyl Alcohol (Methanol) [1] | Acceptable |
| Methyl Ethyl Ketone [1] | Acceptable |
| Methyl Isobutyl Ketone | Acceptable |
| Methyl Mercaptan [2] | Acceptable |
| Methyl Methacrylate [2] | Acceptable |
| Methyl tert-Butyl Ether (MTBE) | Acceptable |
| Methylene Chloride | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| N-Methylpyrrolidinone [1] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Mineral Oil | Acceptable |
| Morpholine | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Motor Oil [1] | Acceptable |
| Naphtha [2] | Acceptable |
| Naphthalene [2] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Nitric Acid [1] | Avoid Extensive Exposure above 0.1% |
| Nitrobenzene [1] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Nitrogen | Acceptable |
| Nitrogen Tetroxide [2] | Avoid Extensive Exposure above 0.1% |
| Nitromethane | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Ozone [1] | Avoid Extensive Exposure above 100 ppm |
| Perchloroethylene [2] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Peroxyacetic Acid [2] | Avoid Extensive Exposure above 1% |
| Peroxybenzoic Acid [2] | Avoid Extensive Exposure above 1% |
| Phenol [1] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Phosphoric Acid [1] | Avoid Use of Mineral Filled Grades |
| Phosphorus Trichloride | Acceptable |
| Potassium Chloride [2] | Acceptable |
| Potassium Dichromate | Avoid Extensive Exposure above 0.1% |
| Potassium Hydroxide [2] | Acceptable |
| Potassium Permanganate | Avoid Extensive Exposure above 0.1% |
| Propane [2] | Acceptable |
| Propyl Mercaptan [2] | Acceptable |
| Propylene [2] | Acceptable |
| Propylene Chlorohydrin [2] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Propylene Glycol Monomethylether [1] | Acceptable |
| Pyridine | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Rapeseed (Rape) Oil [2] | Acceptable |
| Rape Oil Methyl Ester [2] | Acceptable |
| Refrigerant R-22 [1] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Sodium Acetate | Acceptable |
| Sodium Bicarbonate | Acceptable |
| Sodium Bisulfate | Acceptable |
| Sodium Carbonate | Acceptable |
| Sodium Chloride | Acceptable |
| Sodium Cyanide [2] | Acceptable |
| Sodium Dichromate | Avoid Extensive Exposure above 0.1% |
| Sodium Hydrosulfite [2] | Acceptable |
| Sodium Hydroxide [1] | Acceptable |
| Sodium Hypochlorite [1] | Avoid Extensive Exposure above 5% |
| Sodium Nitrate | Acceptable |
| Sodium Sulfate | Acceptable |
| Sodium Sulfide | Acceptable |
| Sodium Thiosulfate | Acceptable |
| Steam | Acceptable |
| Stoddard Solvent | Acceptable |
| Sulfolane | Acceptable |
| Sulfur Dioxide [2] | Acceptable |
| Sulfuric Acid [1] | Avoid Use of Mineral Filled Grades |
| Tetrahydrofuran | Acceptable |
| Thiophenol [2] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Toluene [1] | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Tomato Juice | Acceptable |
| Transmission Fluid [1] | Acceptable |
| Trichloroacetic Acid | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| 1,1,1-Trichloroethane | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Trichloroethylene | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Trichlorotrifluoroethane | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Triethyl Phosphate | Acceptable |
| Triethylamine | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Triphenyl Phosphite | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Trisodium Phosphate | Acceptable |
| Turpentine | Acceptable |
| Vegetable Oil | Acceptable |
| Vinegar | Acceptable |
| Water | Acceptable |
| Water: Salt Water, Sea Water, Tap Water | Acceptable |
| Xylene | Questionable at Elevated Temperatures |
| Zinc Chloride [1] | Acceptable |
Most water-based solutions of acids, bases, or neutral salts have no different effect on Ryton® PPS compounds than water alone. The primary exceptions are strong oxidizing acids, such as nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, or peroxy acids (see Oxidizing Chemicals). Relatively non-oxidizing acids, such as sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid, have little effect on PPS except under very severe conditions, such as high concentration and temperature.
Strong bases, such as concentrated sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide solutions, do not degrade PPS. Acids and bases tend to enhance and accelerate hydrolytic attack of polymer-reinforcement interfaces (see Hot Water), but the ultimate reduction in performance is typically not much worse than what occurs in water alone. We generally do not recommend use of compounds containing mineral fillers in service with strong acids (pH < 2) because of the susceptibility of some mineral fillers to acid digestion.
| Effects of 50% Aqueous Zinc Chloride on Ryton® PPS Compounds | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ryton® PPS Compound Exposure Conditions | Tensile Strength Retained | Weight Change | Transverse Swell |
| R-4-200BL | |||
| 200 hours, 185°F (85°C) | 101% | + 0.1 % | + 0.1 % |
| BR111BL | |||
| 200 hours, 185°F (85°C) | 97% | 0.0 % | 0.0 % |
| Effects of Strong Acids and Strong Bases on Ryton® R-4 PPS | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Exposure Conditions | Tensile Strength Retained | Weight Change | Transverse Swell |
| 37% Hydrochloric Acid | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 61% | + 1.5 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 35% | - 10.2 % | |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 27% | - 0.7 % | |
| 10% Nitric Acid | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 91% | 0.0 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 0% | ----- | |
| 85% Phosphoric Acid | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | 0.0 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 99% | - 0.3 % | |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 89% | - 7.2 % | |
| 30% Sulfuric Acid | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 94% | + 1.3 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 89% | + 1.3 % | |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 61% | + 3.1 % | |
| 50% Sulfuric Acid | |||
| 1 week, 200°F (93°C) | 80% | + 1.8 % | |
| 16 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 69% | + 0.8 % | |
| 52 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 73% | + 1.6 % | |
| 80% Sulfuric Acid | |||
| 1 week, 200°F (93°C) | 85% | + 1.5 % | |
| 16 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 85% | + 0.6 % | |
| 52 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 46% | + 2.1 % | |
| 30% Sodium Hydroxide | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | + 0.1 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 89% | + 10.5% | |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 63% | + 13.0 % |
Extensive test data demonstrates that Ryton® PPS compounds, regardless of the filler and/or additives used, are virtually impervious to all common automotive fuels (including alcohol-containing flex fuels), lubricating oils, transmission fluids, brake fluids, and other hydraulic fluids. Although differences in fillers and additives can affect resistance to engine coolants, Ryton® PPS compounds are generally very resistant to glycol-based and silicone containing coolants, even at elevated temperatures.
Ryton® R-4-220NA is specially formulated for enhanced resistance to the detrimental effects of water at elevated temperatures (see Hot Water), and therefore tends to retain a greater degree of mechanical strength over long-term exposure to high temperature engine coolants, especially the more aggressive "OAT" and "hybrid" type “long-life” engine coolants.
Hot water can have a negative impact on the mechanical properties of glass-fiber reinforced grades. Ryton® PPS polymer is not hydrolyzed by hot water and Ryton® R-4-220NA PPS, Ryton® R-4-220BL PPS and Ryton® R-7-220BL PPS have been specially formulated for enhanced resistance to hot water.
| Effects of Hot Water on Ryton® PPS Compounds | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ryton® PPS Compound Exposure Conditions | Tensile Strength Retained | Weight Change | Transverse Swell |
| Unfilled PPS | |||
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | + 1.9 % | |
| 6 months, 200°F (93°C) | 94% | + 1.8 % | |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 91% | + 2.0 % | |
| 1 week, 300°F (149°C) | 95% | ||
| 4 weeks, 300°F (149°C) | 91% | ||
| 10 days, 350°F (177°C) | 97% | ||
| R-4 | |||
| 48 weeks, 171°F (77°C) | 76% | + 0.4 % | |
| 48 weeks, 185°F (85°C) | 59% | + 0.5 % | |
| 48 weeks, 199°F (93°C) | 52% | + 0.6 % | |
| 1 week, 284°F (140°C) | 51% | + 0.2 % | + 0.2 % |
| 4 weeks, 284°F (140°C) | 44% | + 0.3 % | + 0.0 % |
| 16 weeks, 284°F (140°C) | 46% | + 0.4 % | + 0.4 % |
| R-4XT | |||
| 1 week, 284°F (140°C) | 77% | + 0.2 % | + 0.0 % |
| 4 weeks, 284°F (140°C) | 64% | + 0.2 % | + 0.2 % |
| 16 weeks, 284°F (140°C) | 52% | + 0.3 % | + 0.2 % |
| R-4-220NA | |||
| 1 week, 284°F (140°C) | 97% | + 0.1 % | + 0.1 % |
| 4 weeks, 284°F (140°C) | 86% | + 0.2 % | + 0.0 % |
| 16 weeks, 284°F (140°C) | 81% | + 0.2 % | + 0.2 % |
| BR111 | |||
| 1 week, 284°F (140°C) | 74% | + 0.2 % | + 0.2 % |
| 4 weeks, 284°F (140°C) | 59% | + 0.2 % | + 0.2 % |
| 16 weeks, 284°F (140°C) | 52% | + 0.3 % | + 0.2 % |
| R-7-220BL | |||
| 500 hours, 284°F (140°C) | 80% | + 0.9 % | |
| 1000 hours, 284°F (140°C) | 75% | + 0.9 % | |
| 2000 hours, 284°F (140°C) | 73% | + 0.9 % |
Non-oxidizing organic chemicals generally have little effect on Ryton® PPS compounds, but amines, aromatic compounds, and halogenated compounds may cause some swelling and softening over extended periods of time at elevated temperatures. Ryton® PPS is practically unaffected by many organic chemicals, even under conditions that will dissolve or destroy other plastics, however some classes of organic chemicals can compromise the PPS polymer matrix. Non-aromatic, non-halogenated alcohols, aldehydes, alkanes, alkenes, esters, ethers, and ketones are all generally suitable for service with Ryton® PPS compounds, even at elevated temperatures.
| Effects of Organic Chemicals on Ryton® R-4 PPS Compounds | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Exposure Conditions | Tensile Strength Retained | Weight Change | Transverse Swell |
| Aniline | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | + 1.0 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 86% | + 5.1 % | |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 42% | + 5.7 % | |
| Benzaldehyde | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 97% | + 1.5 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 47% | + 5.7 % | |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 42% | + 6.5 % | |
| Benzonitrile | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | + 0.7 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 79% | + 4.1 % | |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 39% | + 5.5 % | |
| n-Butyl Alcohol | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | 0.0 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 92% | + 0.1 % | |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 80% | 0.0 % | |
| Butyl Ether | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | 0.0 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 89% | + 0.7 % | |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 79% | + 0.8 % | |
| Butylamine | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 96% | + 0.8 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 46% | + 3.5 % | |
| Carbon Tetrachloride | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | + 1.0 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 48% | + 6.5 % | |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 25% | + 9.9 % | |
| Chloroform | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 81% | + 4.0 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 77% | + 9.0 % | |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 43% | + 3.9 % | |
| Cresyl Diphenyl Phosphate | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | + 0.1 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | + 2.2 % | |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 95% | + 0.5 % | |
| Crude Oil (aromatic) | |||
| 4 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 101% | ||
| 16 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 98% | ||
| 52 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | ||
| Cyclohexanol | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | 0.0 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 91% | + 0.2 % | |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 86% | + 0.1 % | |
| 1,2-Dichloroethane | |||
| 2 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 108% | + 4.2 % | + 2.5 % |
| 8 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 96% | + 4.5 % | + 2.8 % |
| 24 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 104% | + 4.3 % | + 2.3 % |
| Diesel Fuel | |||
| 8 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | ||
| 28 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 94% | ||
| 52 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 99% | ||
| 25% Diethanolamine | |||
| 1 week, 212°F (100°C) | 100% | ||
| 4 weeks, 212°F (100°C) | 95% | ||
| p-Dioxane | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 99% | + 1.4 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 96% | + 5.2 % | |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 82% | ||
| Ethyl Acetate | |||
| 2 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 114% | + 0.8 % | + 0.8 % |
| 8 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 111% | + 1.9 % | + 1.3 % |
| 24 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 114% | + 2.0 % | + 1.2 % |
| Ethyl Alcohol | |||
| 2 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | + 0.1 % | - 0.8 % |
| 8 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 102% | + 0.6 % | + 0.7 % |
| 24 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | + 0.9 % | + 0.8 % |
| Freon 113 / 10% Oil | |||
| 4 weeks, 100°F (38°C) | 101% | + 0.1 % | |
| 12 weeks, 100°F (38°C) | 98% | 0.0 % | |
| 24 weeks, 100°F (38°C) | 103% | 0.0 % | |
| Hydraulic Fluid, Aircraft | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | + 0.03 % | |
| 1 weeks, 140°F 60°C) | 95% | + 0.02 % | |
| 3 months, 140°F (60°C) | 99% | - 0.02 % | |
| Methyl Ethyl Ketone | |||
| 2 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 115% | + 1.1 % | + 1.0 % |
| 8 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 112% | + 1.9 % | + 1.7 % |
| 24 weeks, 200°F (93°C) | 115% | + 1.9 % | + 1.6 % |
| N-Methylpyrrolidinone | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | + 1.5 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 92% | + 5.7 % | |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 80% | + 5.0 % | |
| Nitrobenzene | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | + 1.3 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 63% | + 6.6 % | |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 31% | + 7.3 % | |
| Phenol | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | + 0.5 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 92% | + 2.3 % | |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 63% | + 3.1 % | |
| Refrigerant R-22 | |||
| 4 weeks, 165°F (74°C) | 108% | ||
| 8 weeks, 165°F (74°C) | 107% | ||
| 12 weeks, 165°F (74°C) | 121% | ||
| Toluene | |||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 100% | + 1.1 % | |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 70 % | + 4.9 % | |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 41% | + 4.9 % |
Avoid exposure of Ryton® PPS compounds or Ryton® PPS Alloy compounds to these chemicals except at low concentrations or for very brief periods.
Listed below are some of the strong oxidizing agents and oxidizing acids known or expected to attack and degrade polyphenylene sulfide. We generally do not recommend using Ryton® PPS in extensive service with these chemicals. However, service in the presence of many of these chemicals under relatively mild conditions may be acceptable. For example, Ryton® PPS can withstand common disinfectant solutions that contain low concentrations of some these chemicals (such as hydrogen peroxide, sodium hypochlorite, or chlorine). Tests and field service experience have also shown that Ryton® PPS can withstand the small quantities of nitric acid and other acids present in flue gases.
| Nitric Acid Chromic Acid Chlorosulfonic Acid Sodium Hypochlorite Hydrogen Peroxide Potassium Permanganate Potassium Bichromate Sodium Bichromate Ozone | Hydrochloric Acid Hydrobromic Acid Hydrofluoric Acid Chlorine Bromine Iodine Nitrogen Tetroxide Peroxyacetic Acid Peroxybenzoic Acid |
| Effects of Oxidizing Chemicals on Ryton® R-4 PPS | ||
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Exposure Conditions | Tensile Strength Retained | Weight Change |
| 37% Hydrochloric Acid | ||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 61% | +1.5% |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 35% | -10.2% |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 27% | -0.7% |
| 10% Nitric Acid | ||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 91% | 0.0% |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 0% | ---- |
| Ozone, 1.35 ppm | ||
| 4 weeks, 208°F (98°C) | 93% | |
| 5.25% Sodium Hypochlorite | ||
| 24 hours, 200°F (93°C) | 94% | -1.2% |
| 3 months, 200°F (93°C) | 77% | +0.4% |
| 12 months, 200°F (93°C) | 61% | +0.3% |
| Chemical Exposure Conditions | Flexural Strength Retained | Weight Change |
| 1.5% Bromine | ||
| 1 month, 180°F (82°C) | 75% | |
| 2 months, 180°F (82°C) | 60% | -3.1% |
| 3.3% Bromine | ||
| 1 month, 73°F (23°C) | 62% | |
| 3 months, 73°F (23°C) | 36% | -0.8% |
| 0.26% Chlorine | ||
| 1 month, 180°F (82°C) | 85% | |
| 3 months, 180°F (82°C) | 78% | -1.5% |
| 0.7% Chlorine | ||
| 1 month, 73°F (23°C) | 97% | |
| 3 months, 73°F (23°C) | 99% | +1.4% |
Ryton® PPS can withstand both gamma and neutron radiation exposure.
Ryton® PPS compounds are used in many nuclear installation applications because they can withstand both gamma and neutron radiation. The data tabulated below shows that 40% glass fiber reinforced PPS (Ryton® R-4 PPS) and glass and mineral filled PPS (Ryton® R-10 PPS) compounds exhibited no significant deterioration of mechanical properties after relatively high exposures to gamma and neutron radiation. Other 40% glass fiber reinforced PPS or glass and mineral filled PPS compounds would be expected to show similar resistance to degradation by radiation exposure.
Effects of Radiation Exposure on Ryton® PPS Compounds
| Gamma Radiation | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ryton® PPS Compound Exposure Conditions | Tensile Strength Retained | Flexural Strength Retained | Flexural Modulus Retained |
| R-4 | |||
| 5 x 108 rads at 30°C (86°F) | ----- | 103% | 95% |
| 1 x 109 rads at 30°C (86°F) | ----- | 105% | 97% |
| 5 x 109 rads at 30°C (86°F) | ----- | 99% | 96% |
| 3 x 108 rads at 50-55°C (122-131°F) | 100% | 93% | 102% |
| R-10 5002C | |||
| 3 x 108 rads at 50-55°C (122-131°F) | 97% | 99% | 103% |
| R-10 7006A | |||
| 3 x 108 rads at 50-55°C (122-131°F) | 102% | 99% | 101% |
| Neutron Radiation | |||
| Ryton® PPS Compound Exposure Conditions | Tensile Strength Retained | Flexural Strength Retained | Flexural Modulus Retained |
| R-4 | |||
| 5 x 108 rads at 30°C (86°F) | ----- | 101% | 100% |
| 1 x 109 rads at 30°C (86°F) | ----- | 101% | 99% |
| 4 x 108 rads at 50-55°C (122-131°F) | 90% | 86% | 102% |
| R-10 5002C | |||
| 4 x 108 rads at 50-55°C (122-131°F) | 84% | 94% | 100% |
| R-10 7006A | |||
| 4 x 108 rads at 50-55°C (122-131°F) | 87% | 95% | 97% |
Ryton® PPS compounds and Ryton® PPS Alloy compounds are highly resistant to thermal oxidative degradation at elevated temperatures.
Ryton® PPS compounds exhibit exceptional resistance to thermal oxidative degradation during long-term exposure to elevated temperatures. Ryton® PPS Alloy compounds also exhibit excellent performance in this regard. The data tabulated below shows the excellent property retention of Ryton® PPS compounds and Ryton® PPS Alloy compounds after thermal aging in air at various temperatures. In these studies, test specimens were aged in forced draft ovens, and samples were removed periodically and tested for tensile strength, modulus (tensile or flexural) and impact strength (unnotched izod or unnotched charpy impact). Under its Component Recognition Program, Underwriters Laboratories (UL) also maintains documentation of studies of the long-term thermal endurance of Ryton® PPS compounds, and UL has established relative thermal indices (RTIs) of 200°C to 240°C (392°F to 464°F) for almost all Ryton® PPS compounds (see UL Yellow Card Listings).
Effects of Thermal Aging on Ryton® PPS Compounds and Ryton® PPS Alloy Compounds
| Thermal Aging at 150°C | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ryton® PPS Compound Hours at 302°F (150°C) | Tensile Strength Retained | Flexural Modulus Retained | Impact Strength Retained |
| XE5030BL | |||
| 500 hours | 79% | 96% | 97% |
| 3000 hours | 100% | 101% | 93% |
| 5000 hours | 101% | 101% | 92% |
| XE4050BL | |||
| 500 hours | 86% | 100% | 104% |
| 3000 hours | 105% | 103% | 98% |
| 5000 hours | 99% | 102% | 85% |
| Thermal Aging at 165°C | |||
| Ryton® PPS Compound Hours at 329°F (165°C) | Tensile Strength Retained | Flexural Modulus Retained | Impact Strength Retained |
| R-4-200BL | |||
| 500 hours | 100% | 99% | 94% |
| 1000 hours | 96% | 98% | 77% |
| 2000 hours | 97% | 100% | 82% |
| BR111BL | |||
| 500 hours | 105% | 99% | 91% |
| 1000 hours | 102% | 101% | 99% |
| 2000 hours | 99% | 95% | 86% |
| XK2340 | |||
| 500 hours | 84% | 104% | 52% |
| 1000 hours | 82% | 108% | 49% |
| 2000 hours | 76% | 106% | 43% |
| Thermal Aging at 200°C | |||
| Ryton® PPS Compound Hours at 392°F (200°C) | Tensile Strength Retained | Flexural Modulus Retained | Impact Strength Retained |
| R-4-200BL | |||
| 500 hours | 85% | 104% | 67% |
| 1000 hours | 81% | 107% | 66% |
| 2000 hours | 74% | 104% | 56% |
| R-4-200NA | |||
| 2000 hours | 76% | 105% | 54% |
| XK2340 | |||
| 2000 hours | 46% | 110% | 21% |
| XE5030BL | |||
| 2000 hours | 77% | 112% | 39% |
| XE4050BL | |||
| 2000 hours | 81% | 119% | 37% |
| Thermal Aging at 220°C | |||
| Ryton® PPS Compound Hours at 428°F (220°C) | Tensile Strength Retained | Tensile Modulus Retained | Impact Strength Retained |
| R-4-200BL | |||
| 500 hours | 80% | 107% | ----- |
| 1000 hours | 79% | 107% | ----- |
| 3000 hours | 72% | 94% | ----- |
| R-4-220BL | |||
| 500 hours | 82% | 109% | ----- |
| 1000 hours | 77% | 98% | ----- |
| 3000 hours | 76% | 97% | ----- |
| XE5030BL | |||
| 500 hours | 82% | 103% | 45% |
| 1000 hours | 82% | 106% | 43% |
| 2000 hours | 80% | 108% | 40% |
| 3000 hours | 77% | 109% | 37% |
| XE4050BL | |||
| 500 hours | 88% | 105% | 46% |
| 1000 hours | 89% | 108% | 46% |
| 2000 hours | 89% | 113% | 41% |
| 3000 hours | 87% | 114% | 46% |
| Thermal Aging at 240°C | |||
| Ryton® PPS Compound Hours at 464°F (240°C) | Tensile Strength Retained | Flexural Modulus Retained | Impact Strength Retained |
| R-4-200BL | |||
| 504 hours | 75% | 113% | 58% |
| 1002 hours | 75% | 114% | 51% |
| 2112 hours | 69% | 122% | 51% |
| 2994 hours | 65% | 125% | 41% |
| BR111 | |||
| 504 hours | 89% | 103% | 57% |
| 1002 hours | 85% | 100% | 52% |
| 2112 hours | 83% | 110% | 53% |
| 2994 hours | 78% | 114% | 48% |
Although exposure to UV light and weathering may cause some surface degradation and erosion, the mechanical properties of Ryton® PPS will be relatively unaffected.
Although exposure of Ryton® PPS to UV light may cause some surface degradation and erosion, the properties of the bulk material generally are relatively unaffected by such exposure. In the study summarized below, Ryton® R-4 PPS (which has no UV inhibitor) and Ryton® R-4 PPS with 2% carbon black as UV inhibitor were subjected to aging in an Atlas Weatherometer and suffered minimal property loss. Many Ryton® PPS compounds have been rated suitable for outdoor use with respect to UV light exposure, water exposure and water immersion in accordance with UL746C (see UL Yellow Card Listings). However, since some discoloration and attrition of surface material may occur over time with UV exposure and weathering, part surface finish should not be expected to remain unchanged over the long term.
| Effects of Weatherometer Aging on Ryton® PPS Compounds | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ryton® PPS Compound Hours of Exposure | Tensile Strength kpsi | Elongation | Surface Erosion mm |
| R-4 | |||
| 0 | 16.7 | 1.1 % | |
| 2000 | 15.3 | 1.2 % | |
| 6000 | 15.5 | 1.4 % | |
| 8000 | 14.4 | 1.2 % | |
| 10000 | 10.6 | 0.6 % | 0.33 |
| R-4 with 2% Carbon Black | |||
| 0 | 17.4 | 1.2 % | |
| 2000 | 17.3 | 1.1 % | |
| 6000 | 17.3 | 0.9 % | |
| 8000 | 16.8 | 1.0 % | 0.05 |
Engineering Properties
Detailed engineering properties are available for commonly used Ryton® PPS compounds and Ryton® PPS Alloy compounds. These feature industry-standard test methods and typical end-use operating conditions.
If you are unable to locate data for the test method or product required, please contact our technical experts for further assistance.
Thrust Washer Test
The dynamic coefficient of friction and wear rate of Ryton® PPS compounds has been determined using a Thrust Washer machine according to ASTM D 3702. In this test, a specimen having a ring-shaped test surface is rotated against a stationary steel washer at a specified speed and under a specified weight for a specified period of time, and the reduction in thickness of the test specimen is then measured. The dynamic coefficient of friction may also be determined from the torque on the rotating specimen during the test. These tests were performed dry, at 36 rpm (velocity 10 ft/min, 3.05 m/min), under a 50 pound (22.7 kg) test load (250 psi, 1.72 MPa).
Coefficient of Friction and Wear Resistance of Ryton® PPS Compounds
| Ryton® PPS Compound | Countersurface | Test Duration | Material COF | Material Wear Rate | Countersurface Wear Rate | ||
| hours | g/hr | in/hr | mm/hr | g/hr | |||
| R-4 | 52100 Steel (Rc 60) | 10 | 0.50 | 1.2 x 10-2 | 2.2 x 10-3 | 5.5 x 10-2 | 7.0 x 10-3 |
| BR42B | 52100 Steel (Rc 60) | 100 | 0.32 | 3.8 x 10-4 | 6.2 x 10-5 | 1.6 x 10-3 | 3.0 x 10-4 |
| R-4-200NA | 1018 Steel (Rc 20) | 20 | 0.40 | 6.2 x 10-3 | 1.0 x 10-3 | 2.6 x 10-2 | 3.6 x 10-3 |
| R-4-220BL | 1018 Steel (Rc 20) | 20 | 0.43 | 7.4 x 10-3 | 1.3 x 10-3 | 3.3 x 10-2 | 3.9 x 10-3 |
| BR42B | 1018 Steel (Rc 20) | 160 | 0.39 | 3.7 x 10-4 | 6.0 x 10-5 | 1.5 x 10-3 | 2.1 x 10-4 |
Taber Abrasion Test
The abrasion resistance of Ryton® PPS compounds has been determined using the Taber abrasion apparatus according to ASTM D 1044. In this test, a flat plaque test specimen is mounted on a turntable in contact with a weighted abrasive wheel, and after a selected number of revolutions of the wheel at constant speed, the weight loss of the specimen is determined.
| Taber Abrasion Testing of Ryton® PPS Compounds | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight Loss (g) After Indicated Number of Revolutions | |||||||
| Ryton® PPS Compound | Wheel | Load | 500 | 1000 | 1500 | 2000 | 10000 |
| R-4 | CS-10 | 1 kg | ----- | 0.070 | ----- | ----- | ----- |
| R-4-02 | CS-10 | 1 kg | ----- | 0.040 | ----- | ----- | ----- |
| R-4-220NA | CS-10 | 1 kg | ----- | 0.054 | ----- | ----- | ----- |
| R-7-120NA | CS-10 | 1 kg | ----- | 0.064 | ----- | ----- | ----- |
| BR111 | CS-10 | 1 kg | ----- | 0.051 | ----- | ----- | ----- |
| BR42B | CS-10 | 1 kg | ----- | 0.015 | ----- | ----- | ----- |
| XK2340 | CS-10 | 1 kg | ----- | 0.031 | ----- | ----- | ----- |
| R-4-200BL | CS-17 | 1 kg | ----- | 0.057 | ----- | ----- | 0.625 |
| R-4-220BL | CS-17 | 1 kg | 0.040 | 0.056 | 0.066 | 0.077 | ----- |
| R-7-120BL | CS-17 | 1 kg | 0.047 | 0.079 | 0.103 | 0.130 | ----- |
| XE5030BL | CS-17 | 1 kg | ----- | 0.055 | ----- | ----- | 0.632 |
| XE4050BL | CS-17 | 1 kg | ----- | 0.107 | ----- | ----- | 0.976 |
Coefficient of Friction
The coefficient of friction of 40% glass fiber reinforced PPS (Ryton® R-4 PPS) was determined using the Alpha Molykote LFW-1 friction and wear test machine. The flat block test specimens were run against a steel ring at selected speeds under a 15 pound (6.8 kg) load. There appeared to be little difference in the static and dynamic coefficient of friction.
| Coefficient of Friction of 40% Glass Fiber Reinforced PPS | ||
|---|---|---|
| Speed | COF | |
| 0 rpm (static) | 0 ft/min (0 m/min) | 0.50 |
| 100 rpm (dynamic) | 29 ft/min (8.8 m/min) | 0.55 |
| 190 rpm (dynamic) | 55 ft/min (16.8 m/min) | 0.53 |
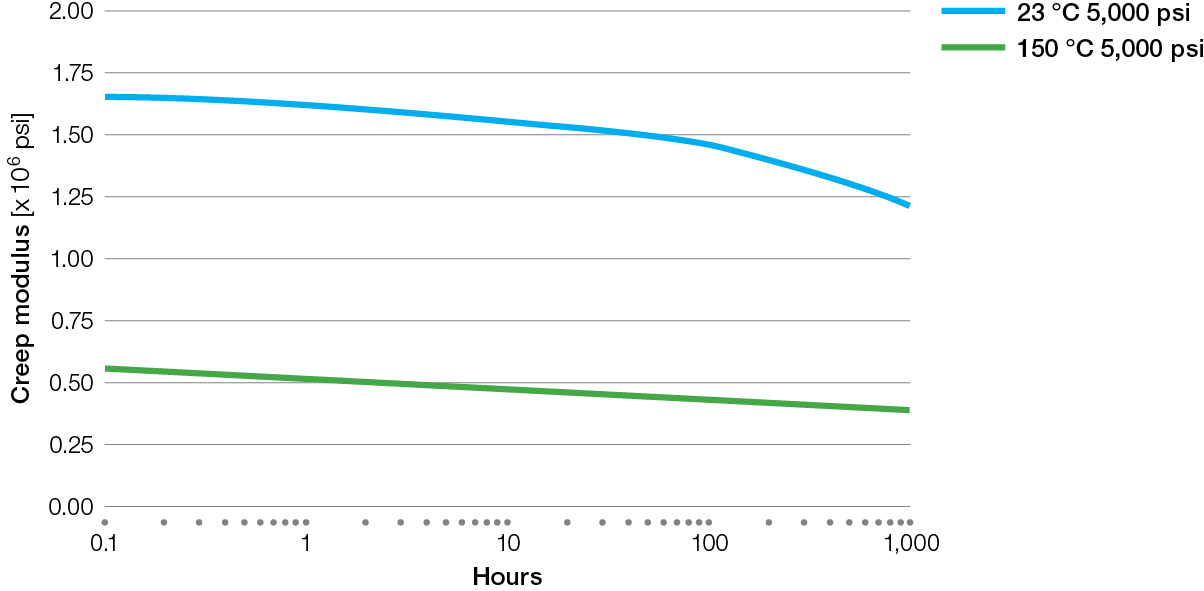
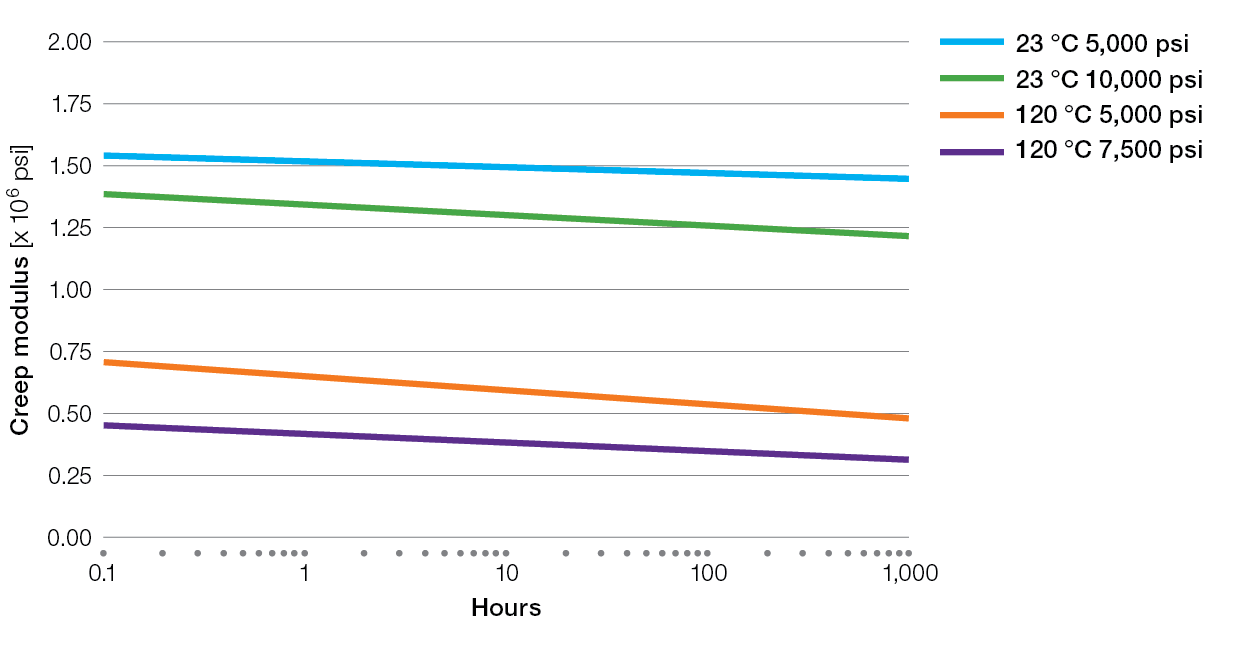
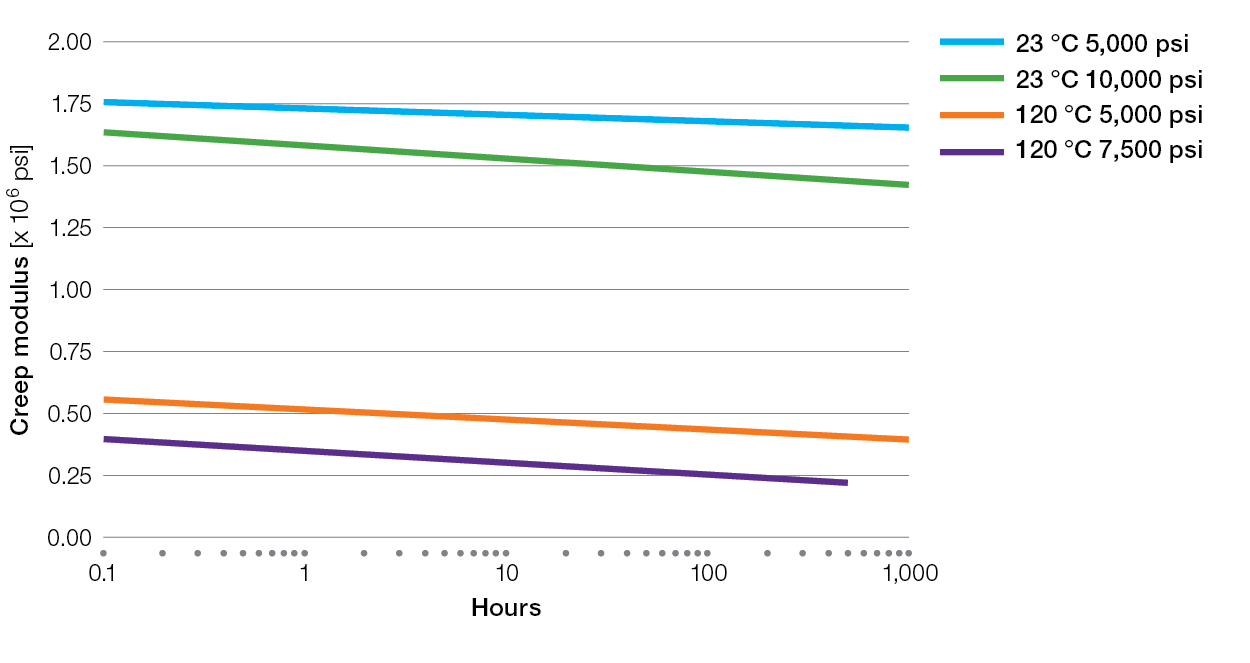
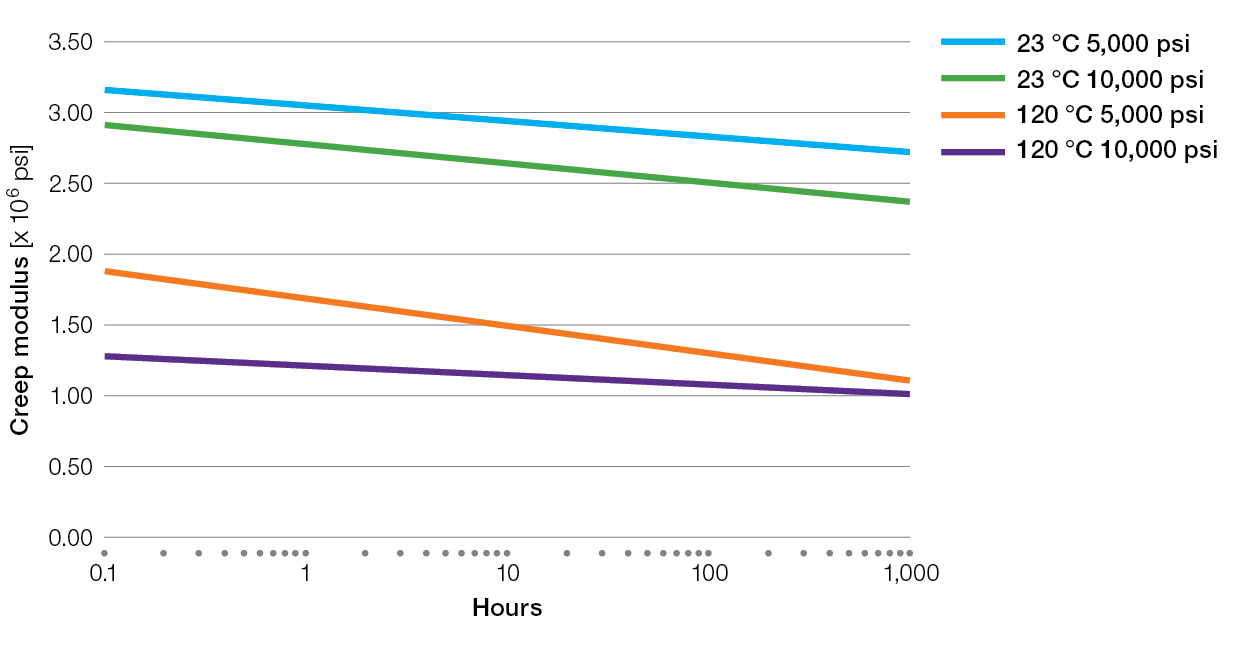
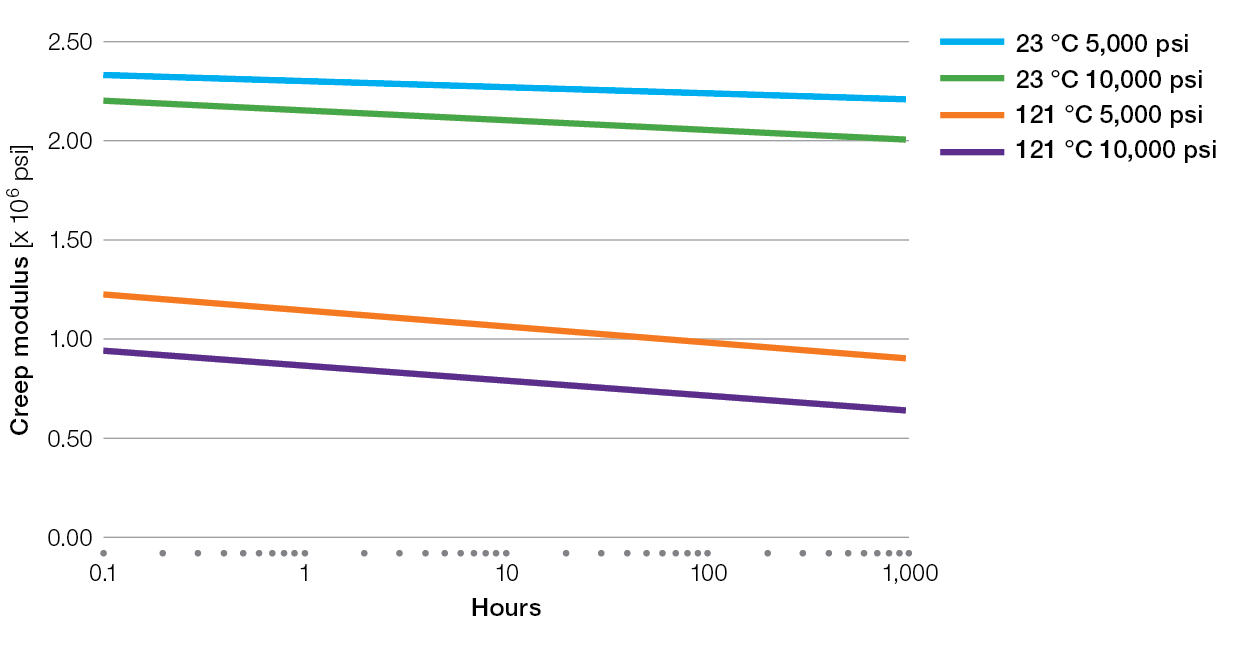
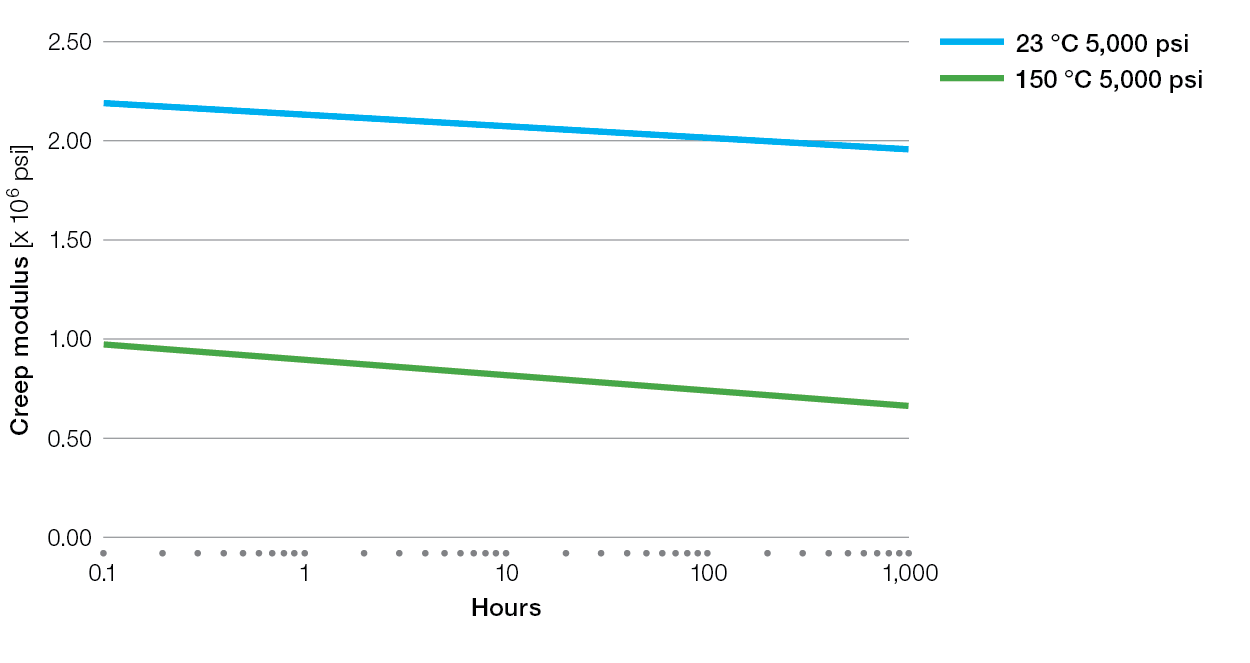
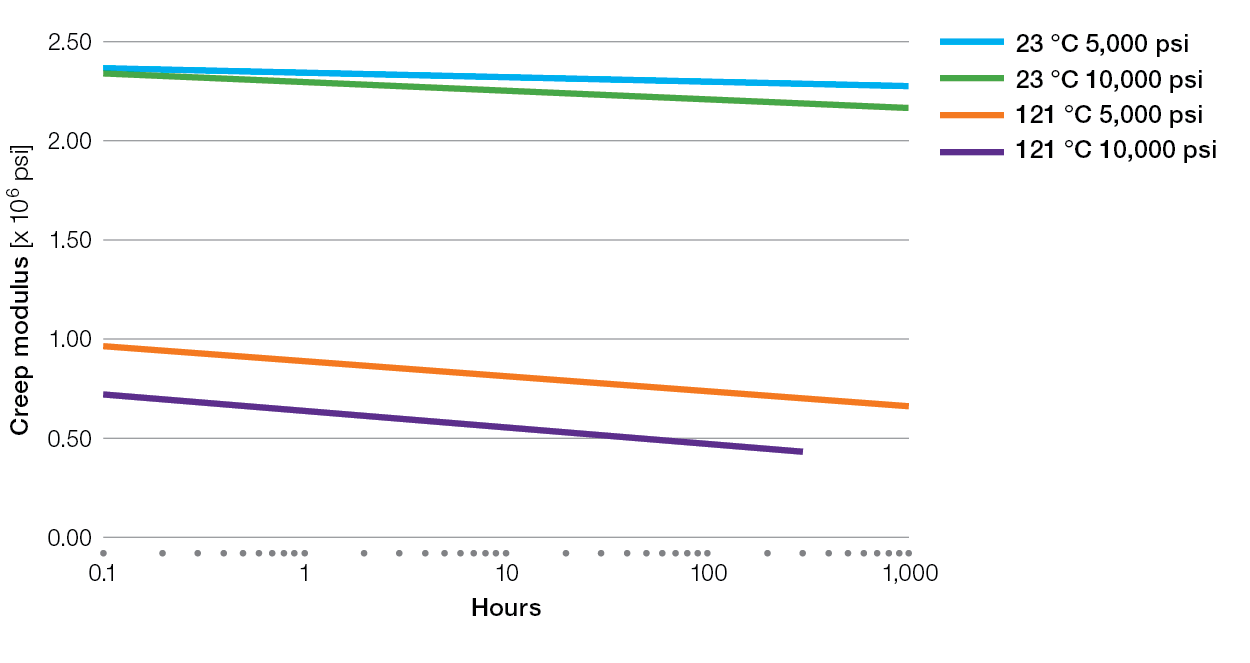
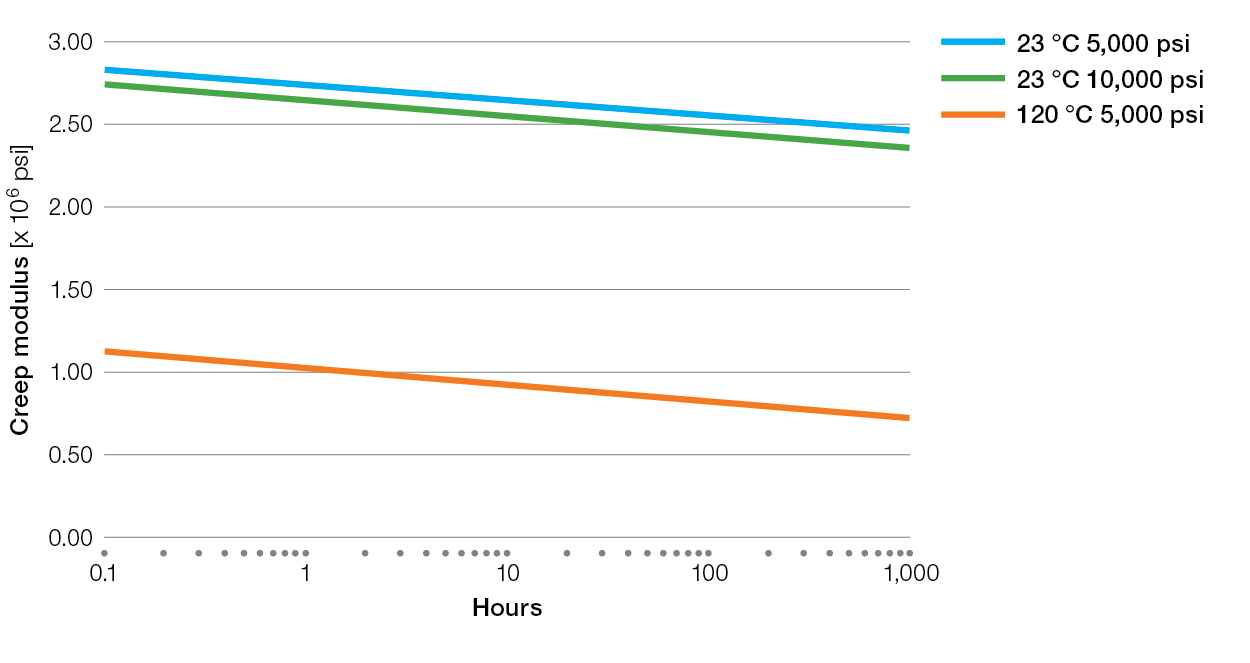
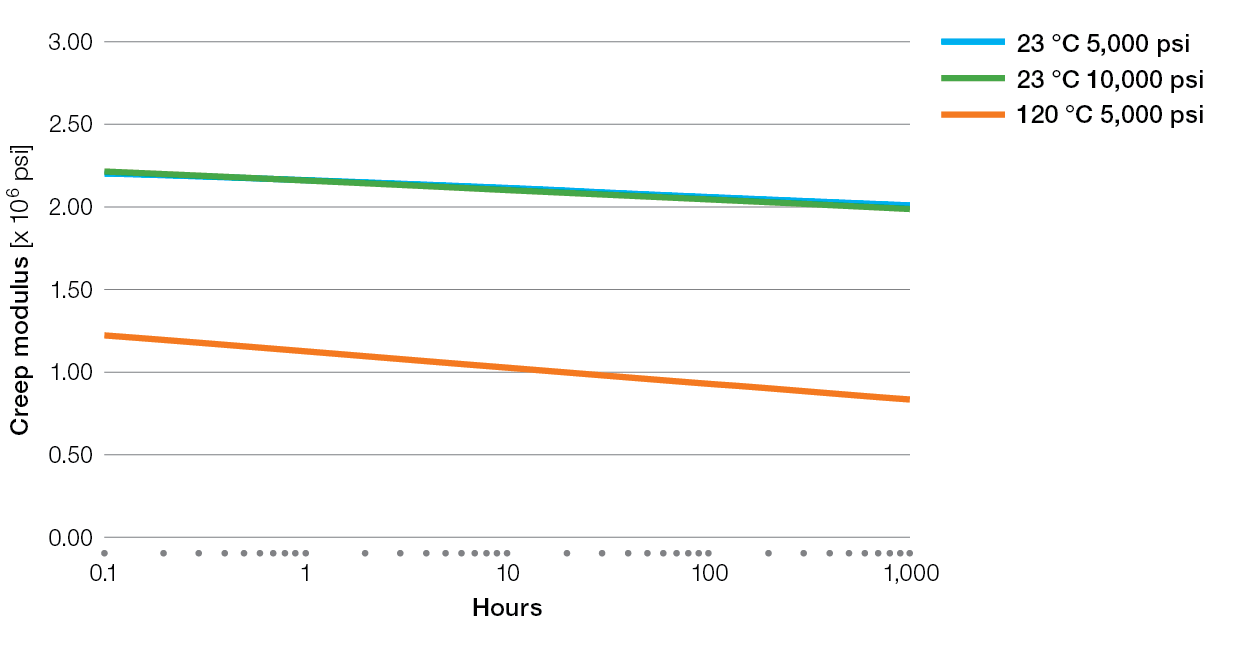
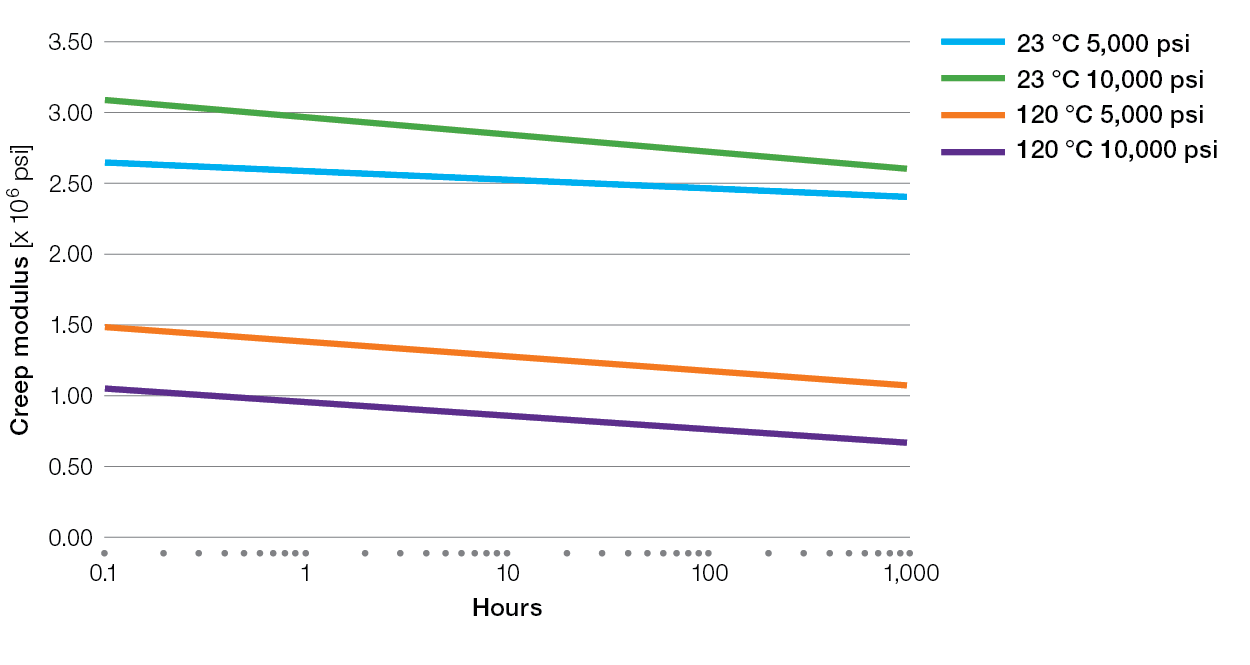
Creep Charts for Ryton® PPS Compounds
XK2340 Tensile Creep
E5030BL Tensile Creep
XE4050BL Tensile Creep
R-7-220BL Tensile Creep
R-4 Tensile Creep
R-7-120BL Tensile Creep
R-4-02XT Tensile Creep
R-4-200BL Tensile Creep
BR42B Tensile Creep
BR111 Tensile Creep
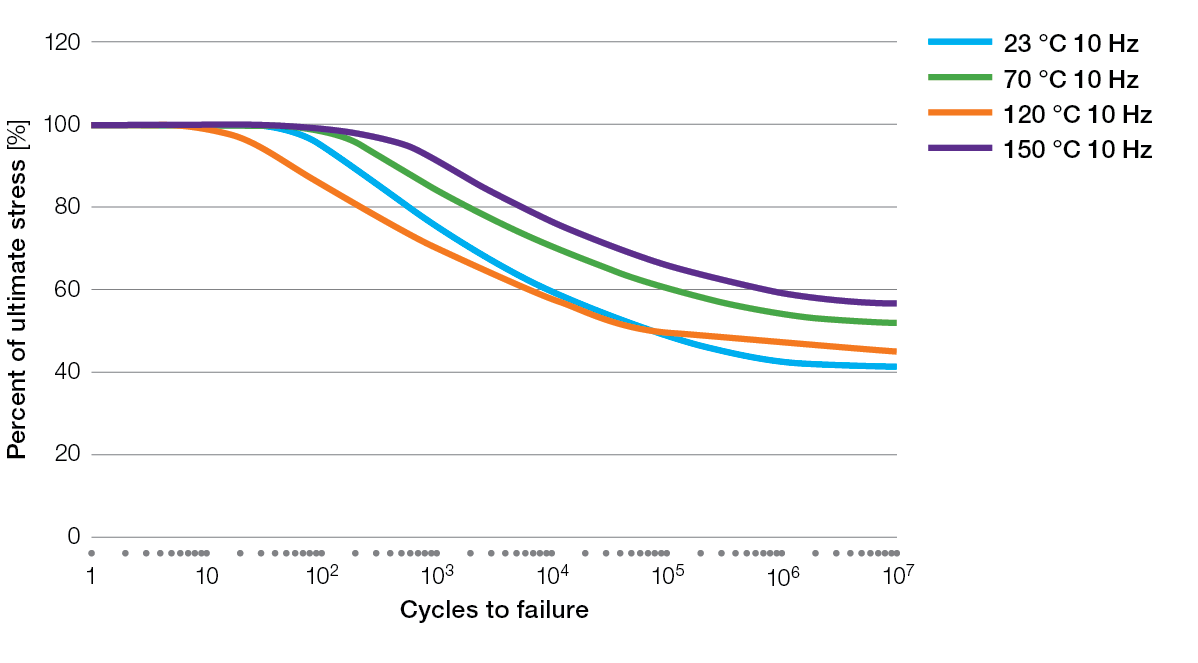
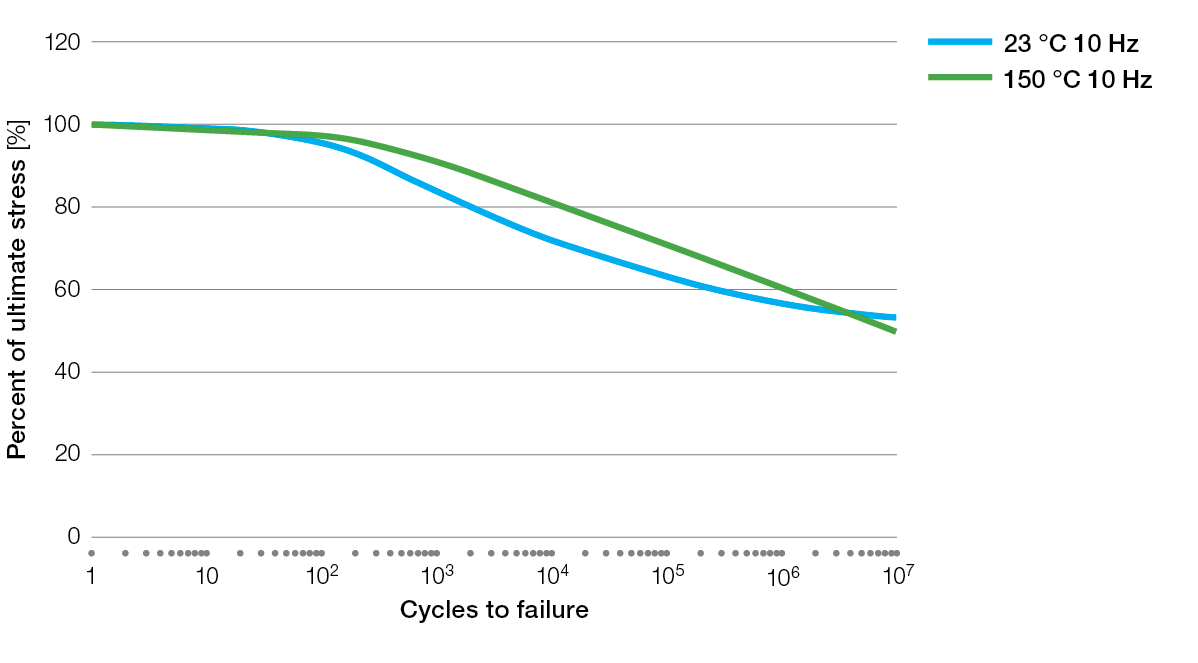
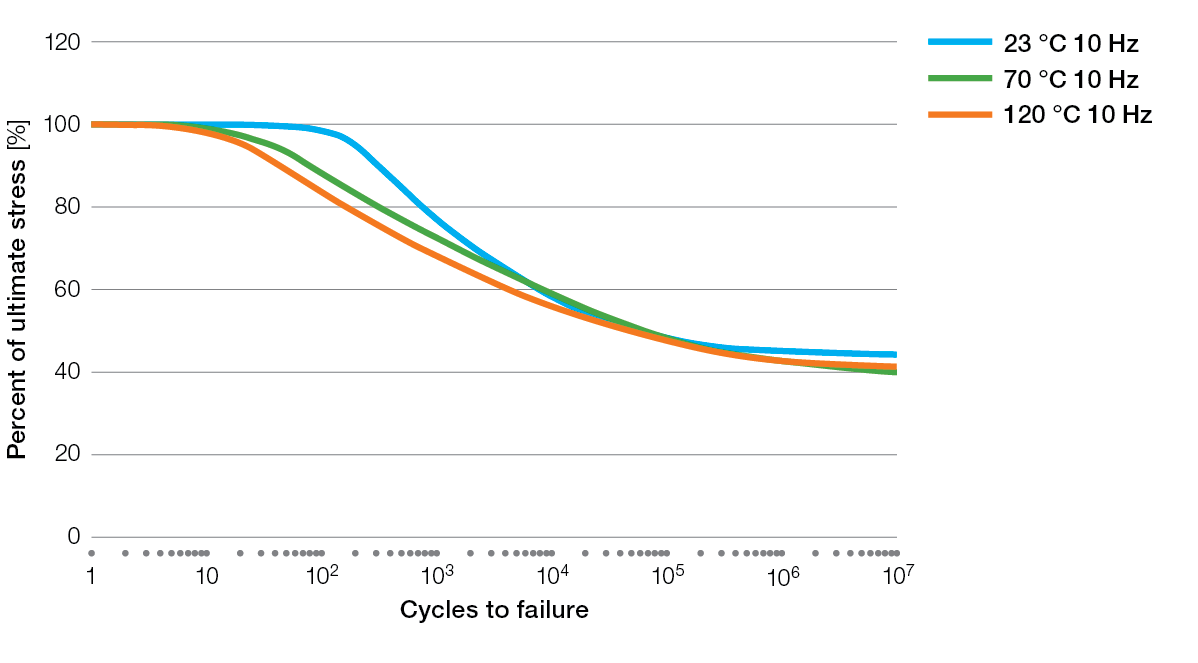
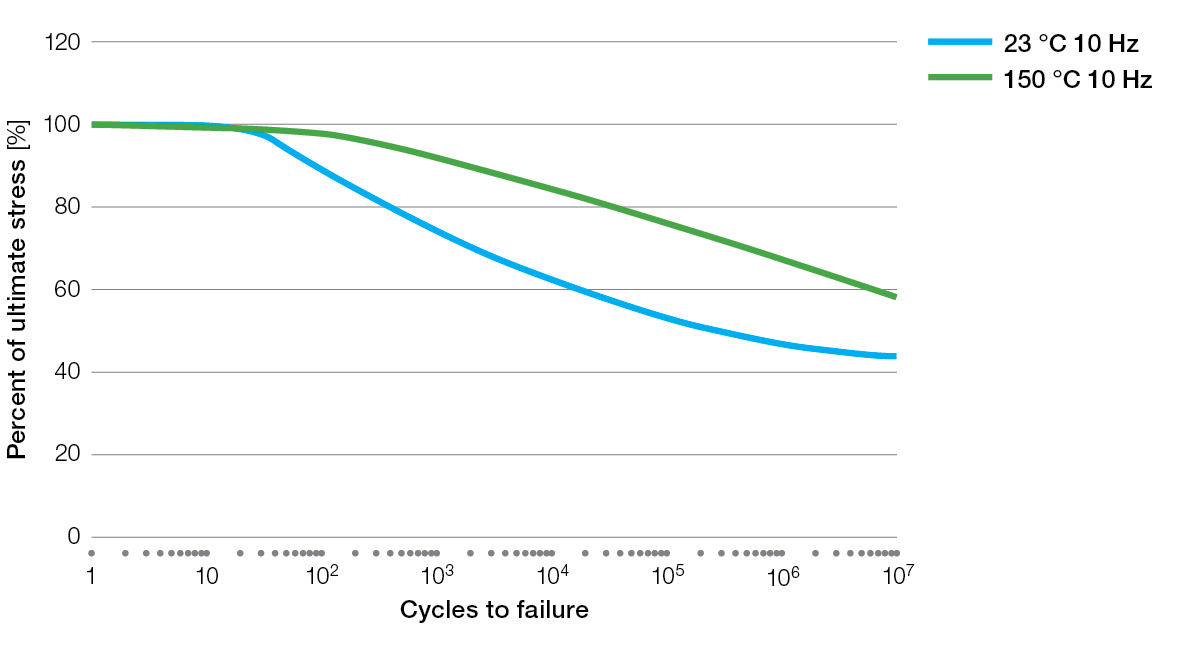
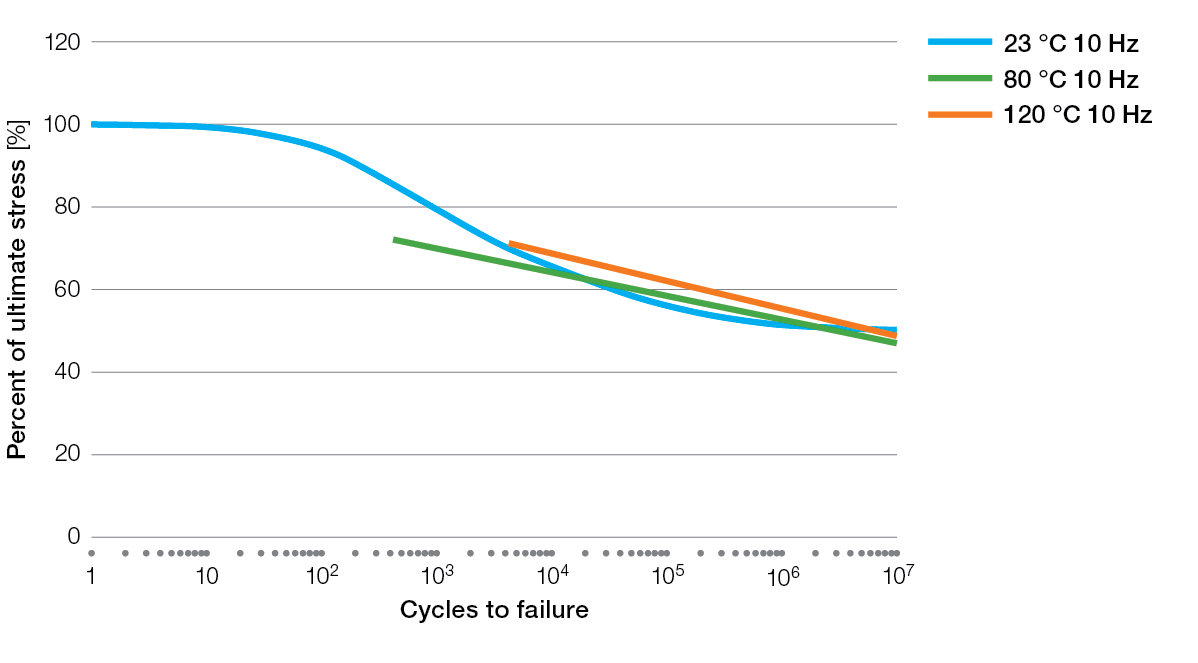
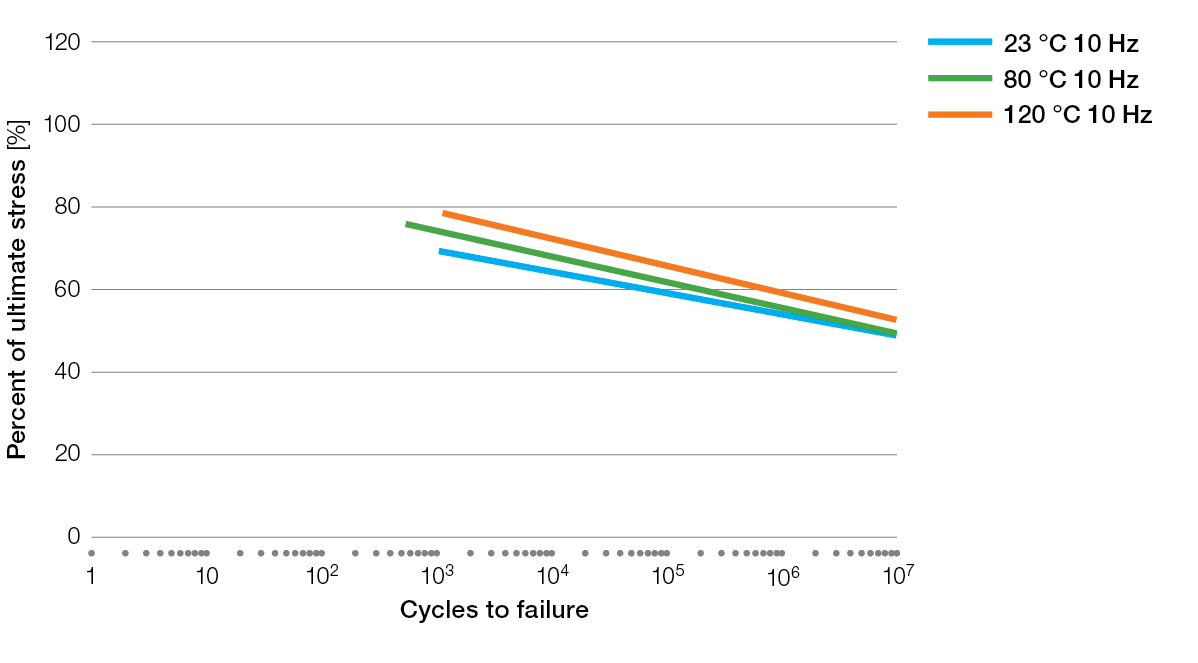
S / N Curves for Ryton® PPS Compounds
BR111 Flexural Fatigue
BR111 Tensile Fatigue
BR42B Flexural Fatigue
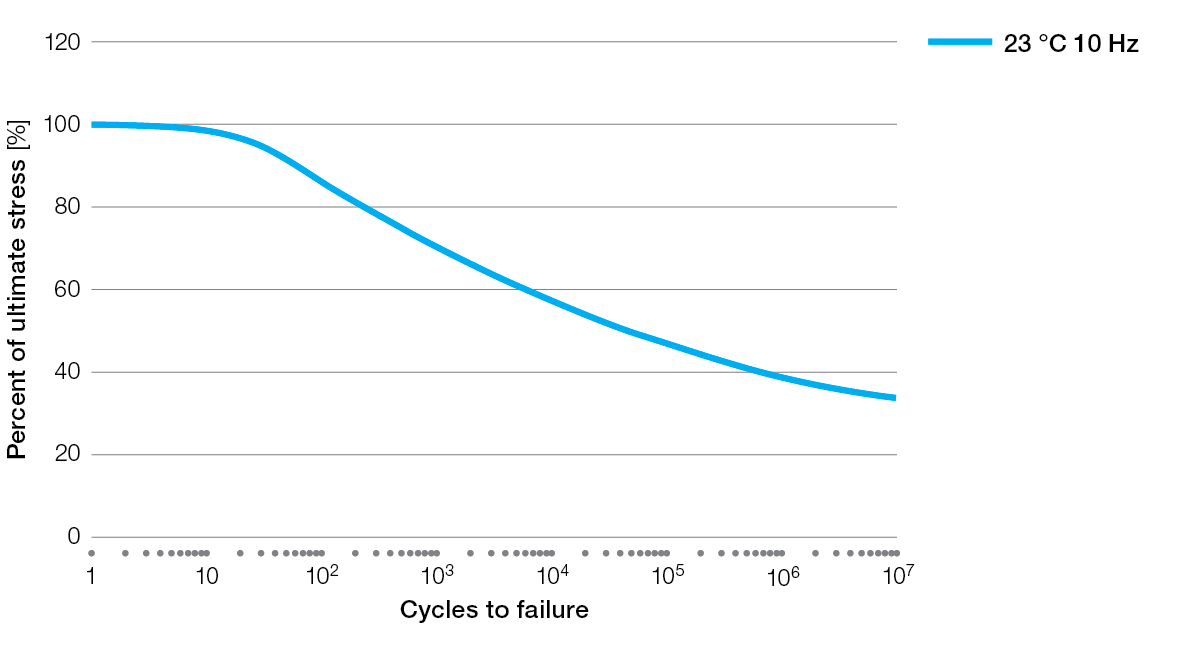
R-4 Tensile Fatigue
R-4-02XT Tensile Fatigue
R-4-200BL Tensile Fatigue
R-7-120BL Tensile Fatigue
Mechanical Properties of Ryton® PPS Compounds at Various Temperatures
Tensile Strength
Nominal Tensile Strength of Ryton® PPS Compounds from -40°C to 200°C
| Ryton® PPS Compound | -40°C -40°F | 23°C 73°F | 50°C 122°F | 75°C 167°F | 100°C 212°F | 150°C 302°F | 200°C 392°F | |
| R-4-200BL | MPa | 195 | 180 | 160 | 140 | 105 | 65 | 45 |
| kpsi | 28 | 26 | 23 | 20 | 15 | 9,5 | 6,5 | |
| R-4-220BL | MPa | 190 | 175 | 160 | 145 | 110 | 65 | 50 |
| kpsi | 28 | 25 | 23 | 21 | 16 | 9,5 | 7,5 | |
| R-4-230BL | MPa | 135 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 110 | 70 | 45 |
| kpsi | 20 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 16 | 10 | 6,5 | |
| R-4-240BL | MPa | 195 | 165 | 150 | 130 | 100 | 60 | 45 |
| kpsi | 28 | 24 | 22 | 19 | 15 | 8,5 | 6,5 | |
| R-7-120BL | MPa | 175 | 135 | 120 | 120 | 100 | 70 | 50 |
| kpsi | 25 | 20 | 17 | 17 | 15 | 8,5 | 6,5 | |
| R-7-220BL | MPa | 185 | 160 | 150 | 140 | 115 | 80 | 60 |
| kpsi | 27 | 23 | 22 | 20 | 17 | 12 | 8,5 | |
| BR111BL | MPa | 220 | 190 | 165 | 155 | 120 | 75 | 55 |
| kpsi | 32 | 28 | 24 | 23 | 17 | 11 | 8.0 | |
| BR42B | MPa | 220 | 190 | 165 | 155 | 120 | 75 | 55 |
| kpsi | 32 | 28 | 24 | 23 | 17 | 11 | 8.0 | |
| XE5030BL | MPa | 160 | 130 | 110 | 95 | 75 | 45 | 35 |
| kpsi | 23 | 19 | 16 | 14 | 11 | 7.5 | 6.0 | |
| XK2340 | MPa | 205 | 195 | 165 | 140 | 120 | 90 | 75 |
| kpsi | 30 | 28 | 24 | 20 | 17 | 13 | 11 |
Test Method: ISO 527
Test Specimen Molding Conditions: Melt Temperature 315-343°C (600-650°F); Mold Temperature 135°C (275°F)
THE NOMINAL PROPERTIES REPORTED HEREIN ARE TYPICAL OF THE PRODUCTS BUT DO NOT REFLECT NORMAL TESTING VARIANCES AND THEREFORE SHOULD NOT BE USED FOR SPECIFICATION PURPOSES.
Tensile Modulus
Nominal Tensile Modulus of Ryton® PPS Compounds from -40°C to 200°C
| Ryton® PPS Compound | -40°C -40°F | 23°C 73°F | 50°C 122°F | 75°C 167°F | 100°C 212°F | 150°C 302°F | 200°C 392°F | |
| R-4-200BL | GPa | 16 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 12 | 7.0 | 5.0 |
| Mpsi | 2.4 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 1.8 | 1.0 | 0.7 | |
| R-4-220BL | GPa | 15 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 11 | 6.0 | 5.5 |
| Mpsi | 2.2 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 1.6 | 0.9 | 0.8 | |
| R-4-230BL | GPa | 16 | 14 | 15 | 14 | 11 | 7.0 | 5.5 |
| Mpsi | 2.4 | 2.1 | 2.2 | 2.1 | 1.6 | 1.0 | 0.8 | |
| R-4-240BL | GPa | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 10 | 5.0 | 4.0 |
| Mpsi | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.5 | 0.7 | 0.6 | |
| R-7-120BL | GPa | 21 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 7.0 | 6.5 |
| Mpsi | 3.1 | 2.8 | 2.6 | 2.5 | 2.4 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |
| R-7-220BL | GPa | 17 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 12 | 8.0 | 7.0 |
| Mpsi | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 1.8 | 1.2 | 1.0 | |
| BR111BL | GPa | 20 | 21 | 20 | 20 | 15 | 8.5 | 7.5 |
| Mpsi | 2.9 | 3.1 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 2.2 | 1.2 | 1.1 | |
| BR42B | GPa | 17 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 12 | 7.5 | 6.0 |
| Mpsi | 2.5 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 1.1 | 0.9 | |
| XE5030BL | GPa | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 7.0 | 4.0 | 3.5 |
| Mpsi | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.5 | |
| XE4050BL | GPa | 12 | 11 | 11 | 10 | 7.5 | 4.0 | 3.5 |
| Mpsi | 1.8 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.1 | 0.6 | 0.5 | |
| XK2340 | GPa | 18 | 15 | 12 | 11 | 9.5 | 7.5 | 7.0 |
| Mpsi | 2.6 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.1 | 1.0 |
Test Method: ISO 527
Test Specimen Molding Conditions: Melt Temperature 315-343°C (600-650°F); Mold Temperature 135°C (275°F)
THE NOMINAL PROPERTIES REPORTED HEREIN ARE TYPICAL OF THE PRODUCTS BUT DO NOT REFLECT NORMAL TESTING VARIANCES AND THEREFORE SHOULD NOT BE USED FOR SPECIFICATION PURPOSES.
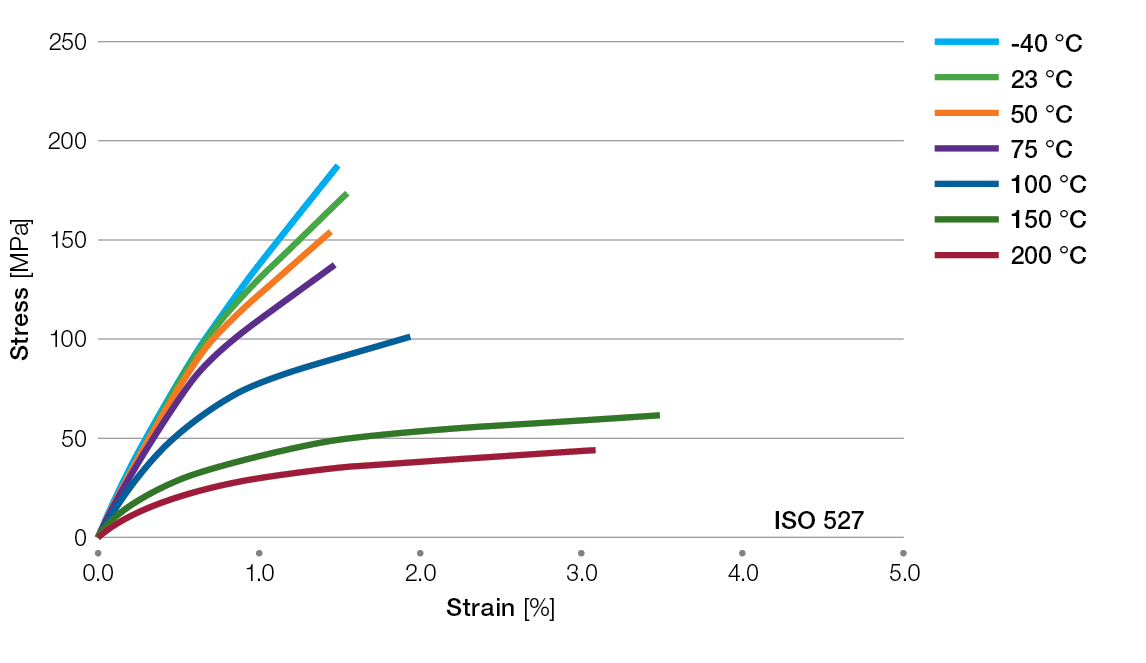
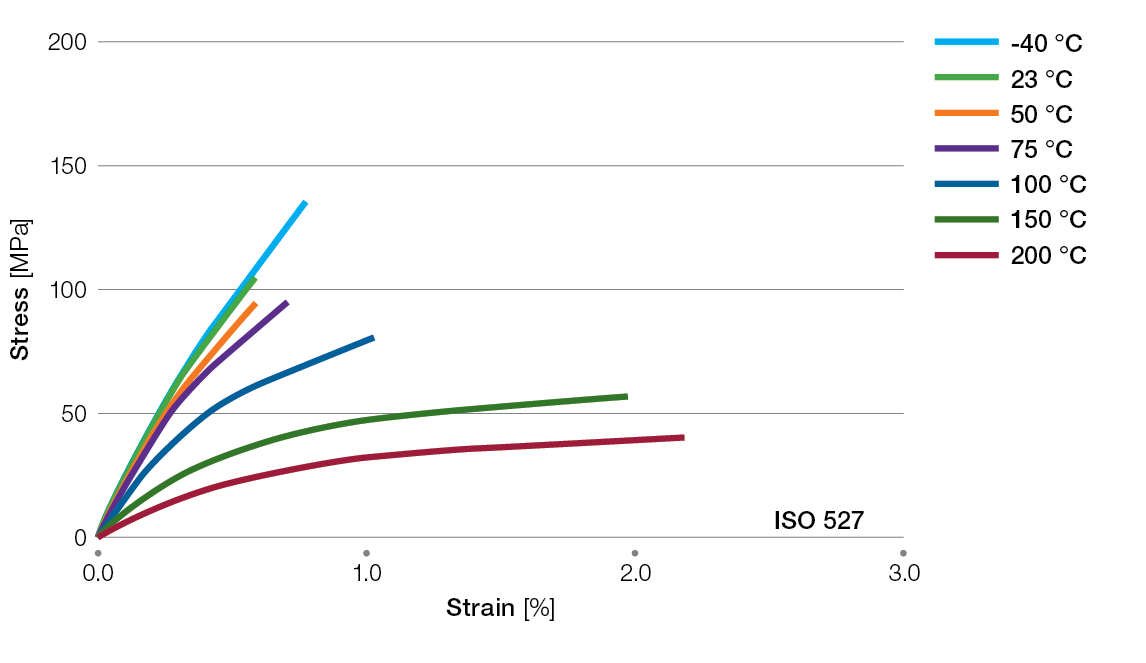
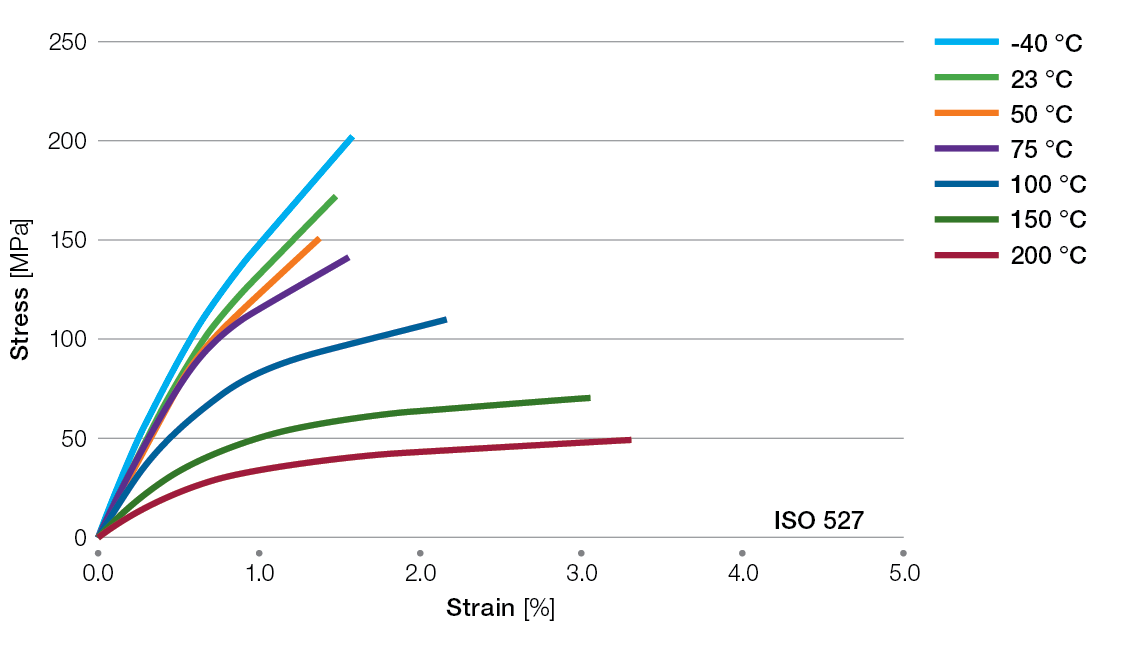
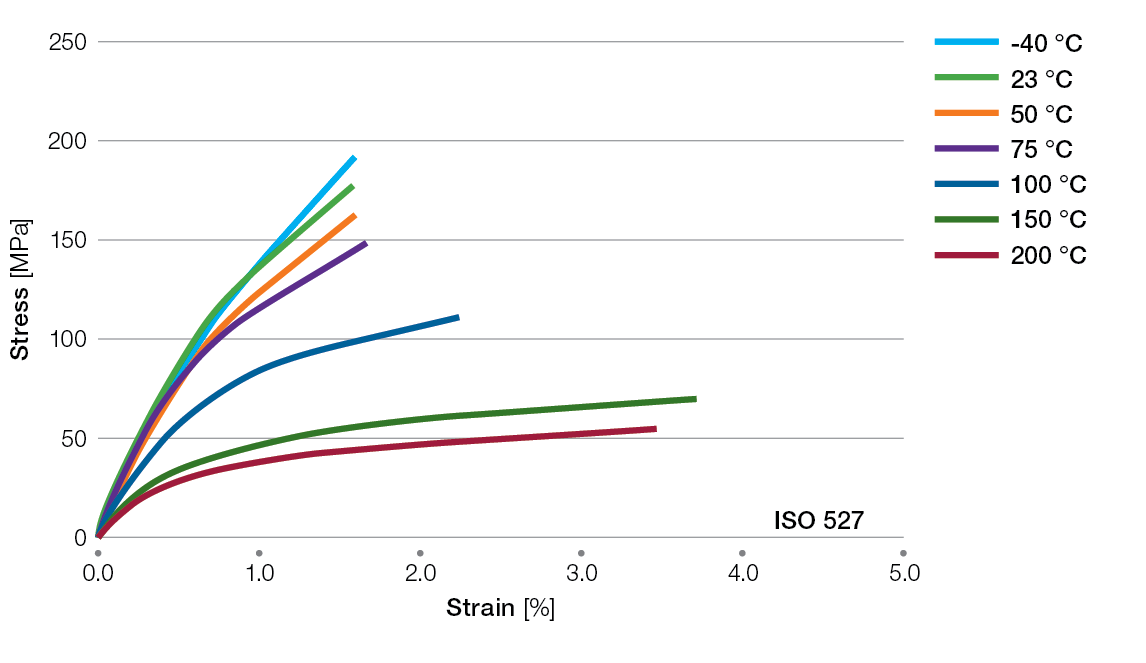
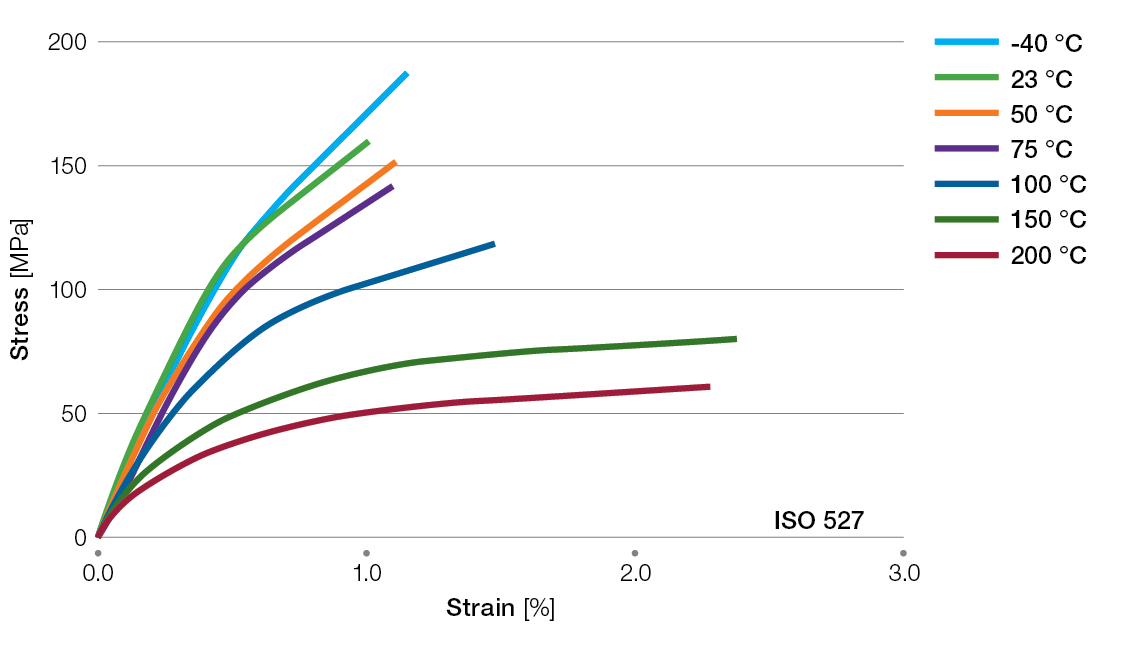
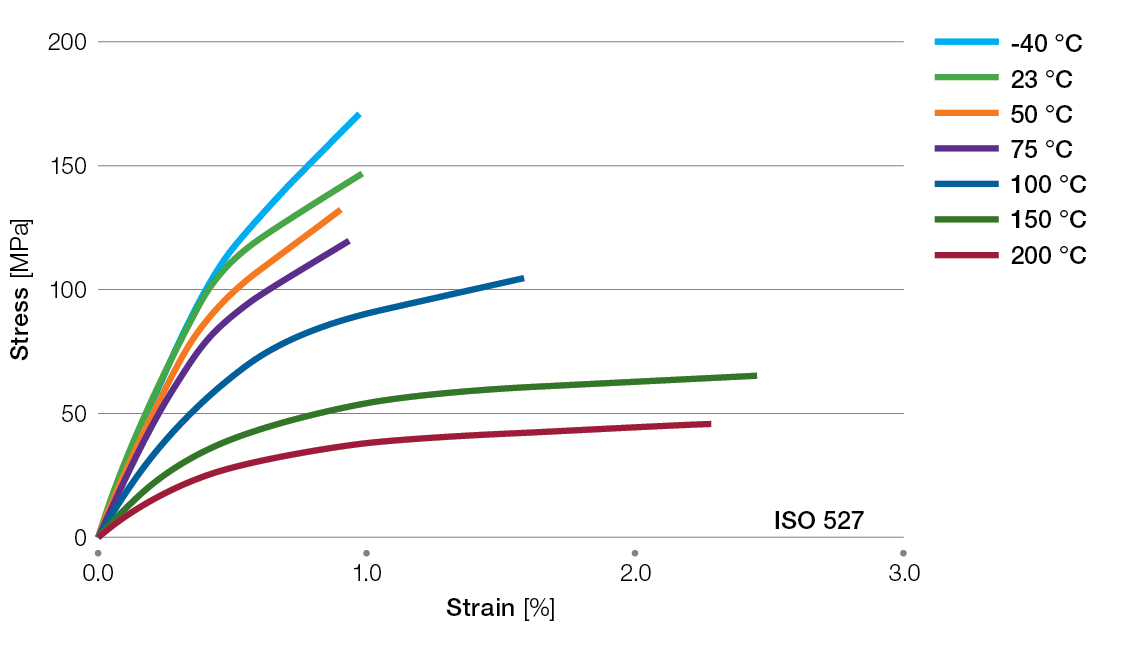
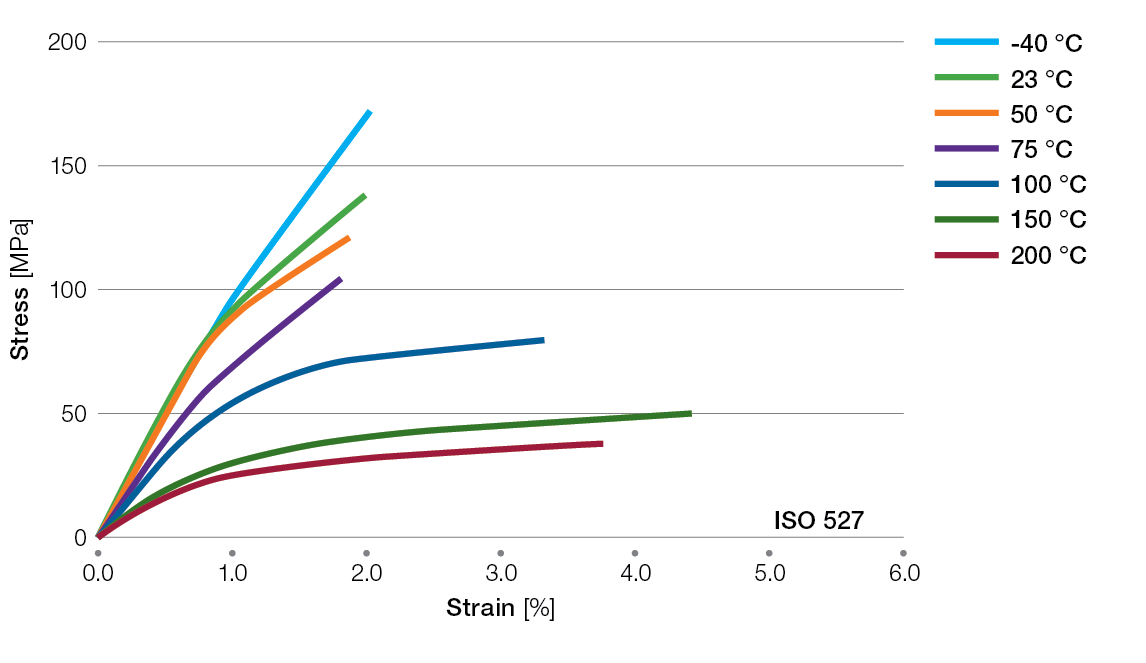
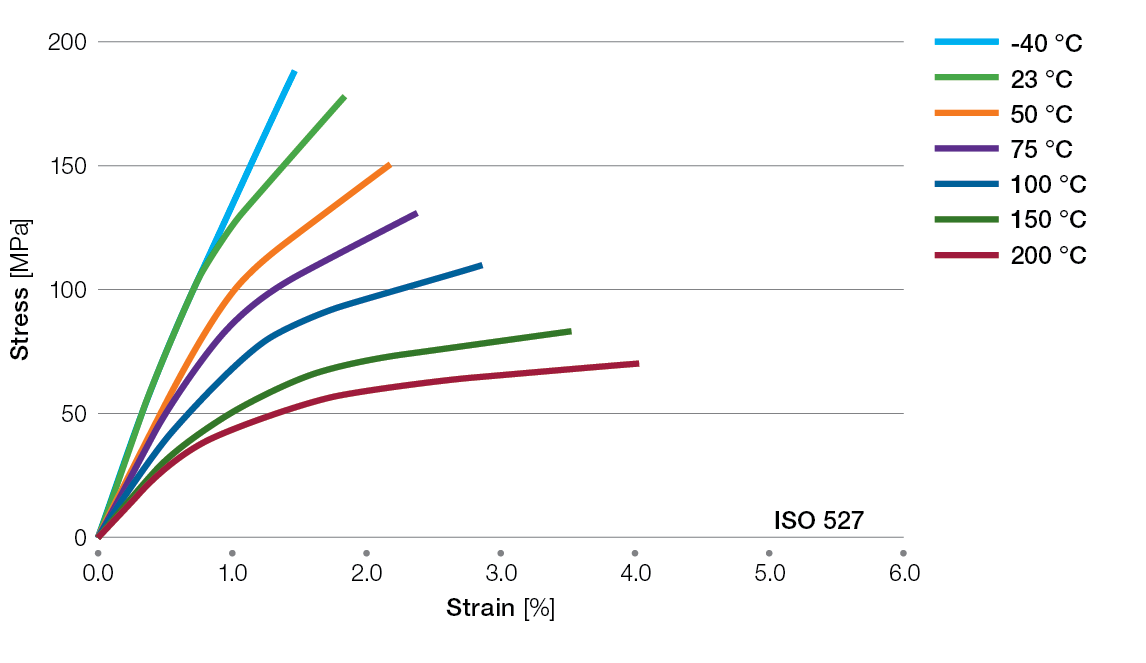
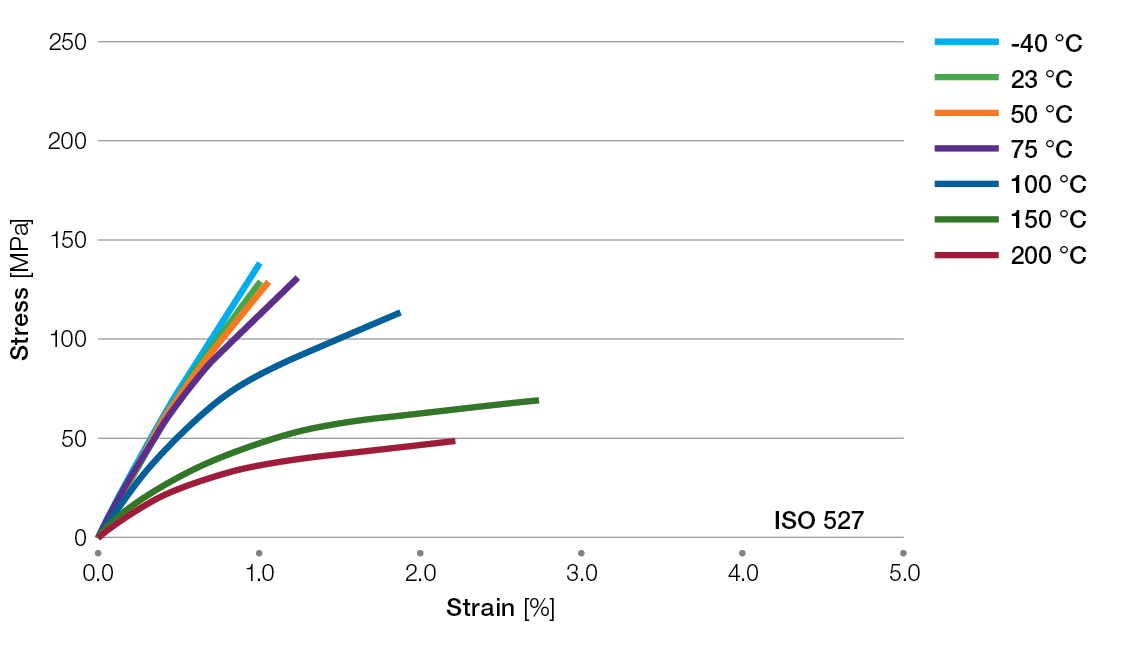
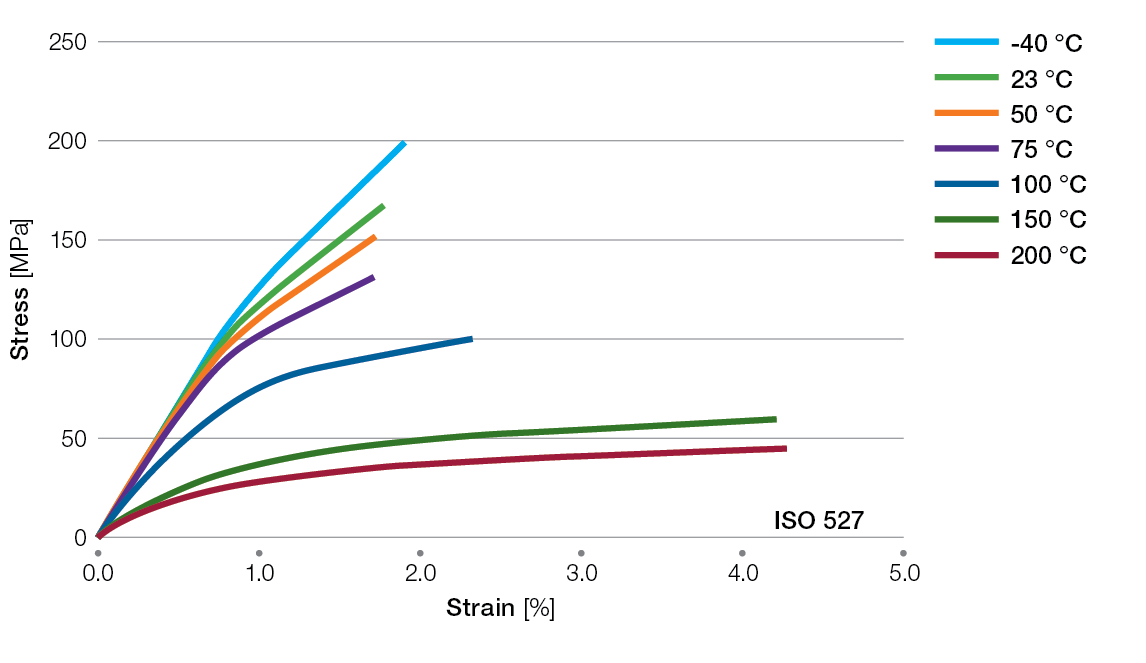
Stress / Strain Curves for Ryton® PPS Compounds
R-4-200BL Tensile Stress/Strain Curves
R-7-120BL Tensile Stress/Strain Curves
BR42B Tensile Stress/Strain Curves
R-4-220BL Tensile Stress/Strain Curves
R-7-220BL Tensile Stress/Strain Curves
BR111BL Tensile Stress/Strain Curves
XE4050BL Tensile Stress/Strain Curves
XE5030BL Tensile Stress/Strain Curves
XK2340 Tensile Stress/Strain Curves
R-4-230BL Tensile Stress/Strain Curves
R-4-240BL Tensile Stress/Strain Curves
Weld Line Strength
Weld lines are formed during the molding process when the melt flow front divides and then flows back together. Typically, the weld line interface is resin rich because the glass fibers tend not to cross the interface. The lack of glass fiber reinforcement across the interface results in lower mechanical strength along the weld line. Gate location and fill patterns should be planned so that weld lines will be eliminated or located in areas of minimal stress whenever possible.
If weld lines must bear stress, the part design should compensate for the typical weld line strengths indicated below. Weld line strength is highly dependent on molding conditions, so the part and tool design should allow for rapid injection, a hot flow front, and thorough packing. Gas entrapment is very detrimental to weld line strength, so molds must be designed to avoid back filling and should be adequately vented in areas where weld lines form.
| Nominal Weld Line Tensile Strength of Ryton® PPS Compounds | ||
|---|---|---|
| BR111 and BR111BL | 45 MPa | 6.5 kpsi |
| BR42B | 55 MPa | 8.0 kpsi |
| R-4 and R-4-02 | 40 MPa | 6.0 kpsi |
| R-4-200NA and R-4-200BL | 60 MPa | 8.5 kpsi |
| R-4-220NA and R-4-220BL | 55 MPa | 8.0 kpsi |
| R-4-230NA and R-4-230BL | 40 MPa | 6.0 kpsi |
| R-4-240NA and R-4-240BL | 80 MPa | 11.5 kpsi |
| R-4XT and R-4-02XT | 55 MPa | 8.0 kpsi |
| R-7-120NA and R-7-120BL | 45 MPa | 6.5 kpsi |
| R-7-121NA and R-7-121BL | 40 MPa | 6.0 kpsi |
| R-7-220BL | 45 MPa | 6.5 kpsi |
| XE4050BL | 45 MPa | 6.5 kpsi |
| XE5030BL | 50 MPa | 7.5 kpsi |
| XE5515BL | 65 MPa | 9.5 kpsi |
| XK2340 | 60 MPa | 8.5 kpsi |
Test Method: ISO 527, double end gated specimens
Test Specimen Molding Conditions: Melt Temperature 315-343°C (600-650°F); Mold Temperature 135°C (275°F)
THE NOMINAL PROPERTIES REPORTED HEREIN ARE TYPICAL OF THE PRODUCTS BUT DO NOT REFLECT NORMAL TESTING VARIANCES AND THEREFORE SHOULD NOT BE USED FOR SPECIFICATION PURPOSES.
Find Ryton® PPS grades, technical data sheets, SDS and more
Find Ryton® PPS products by chemistry, market, application, etc.